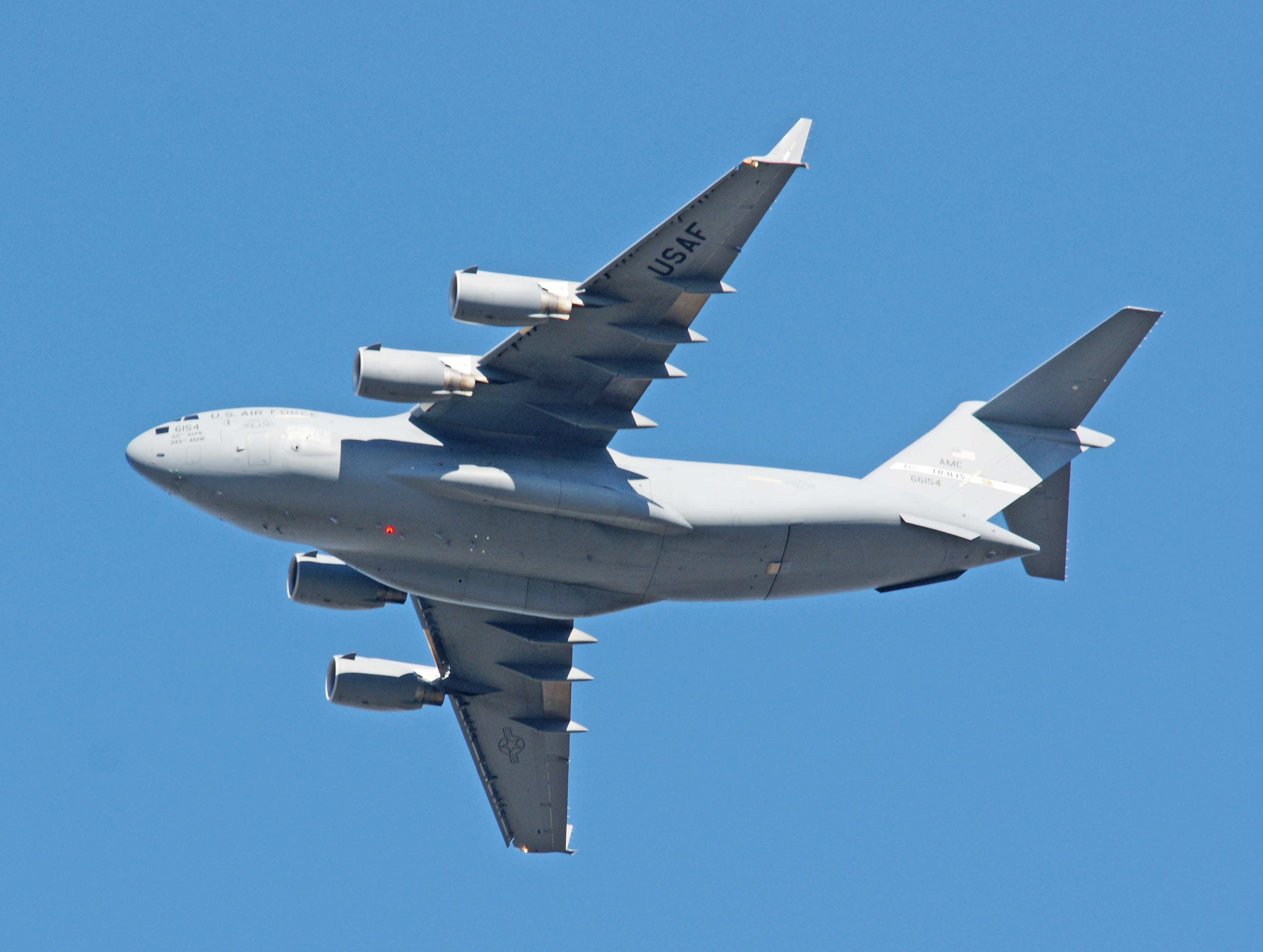
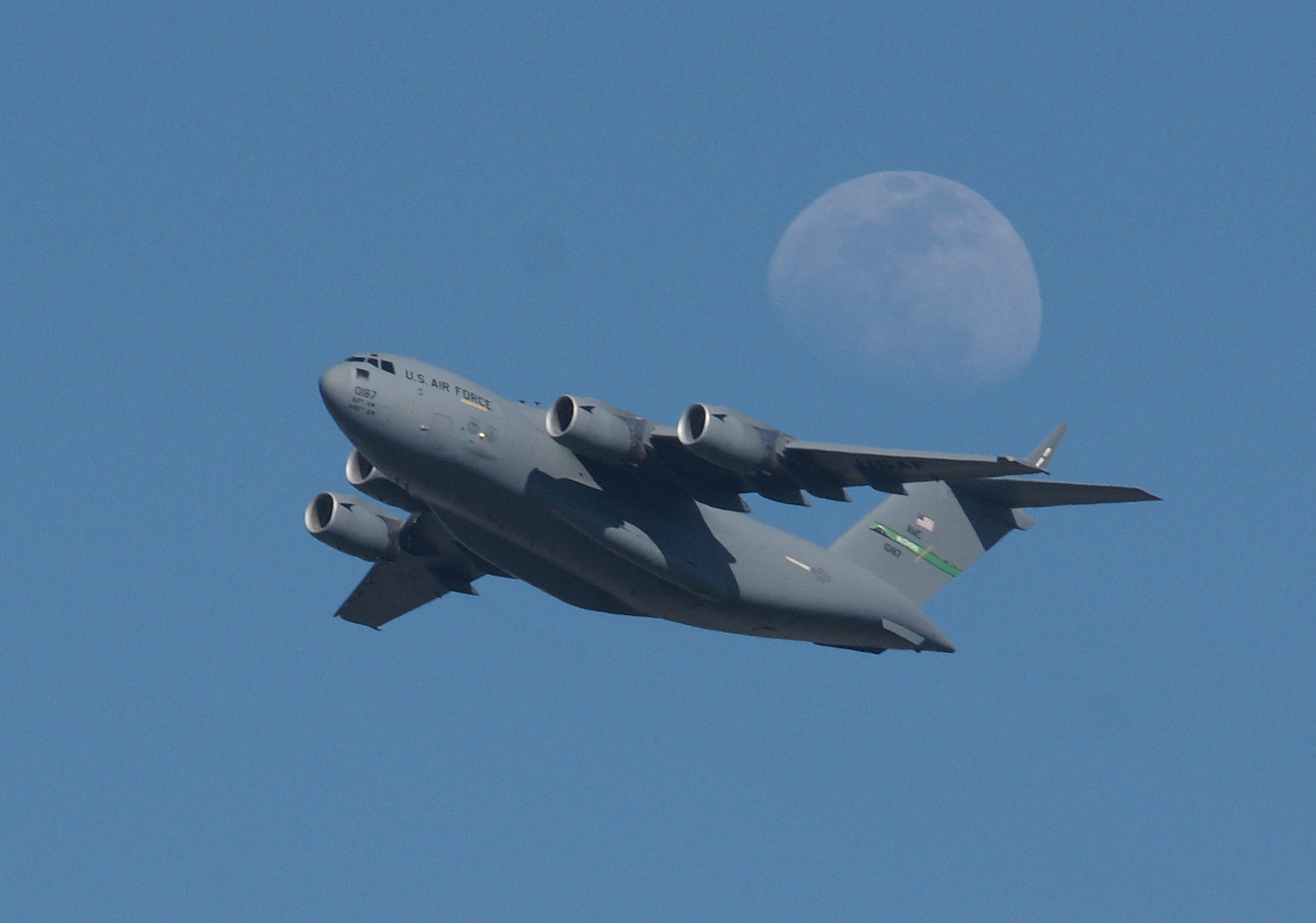
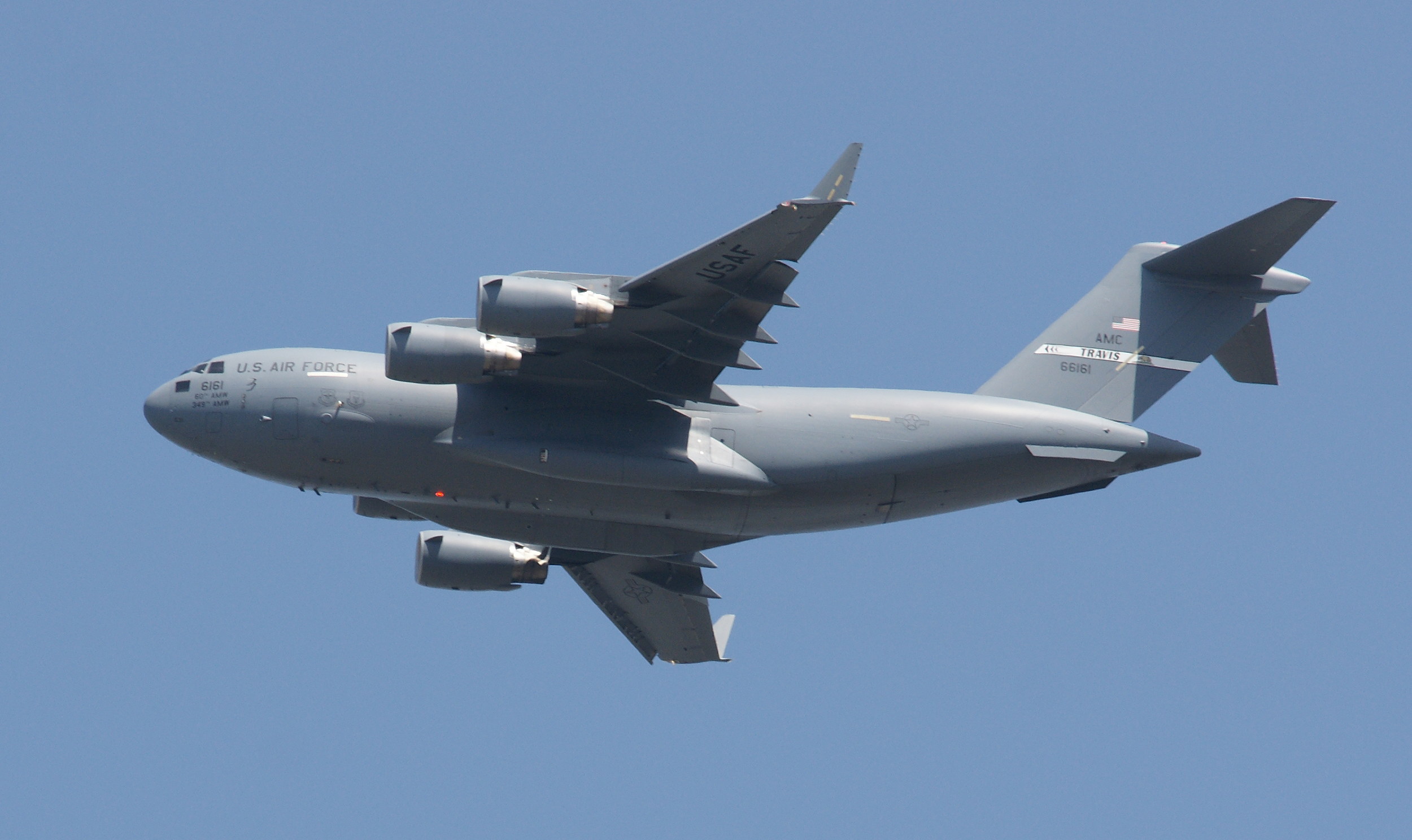
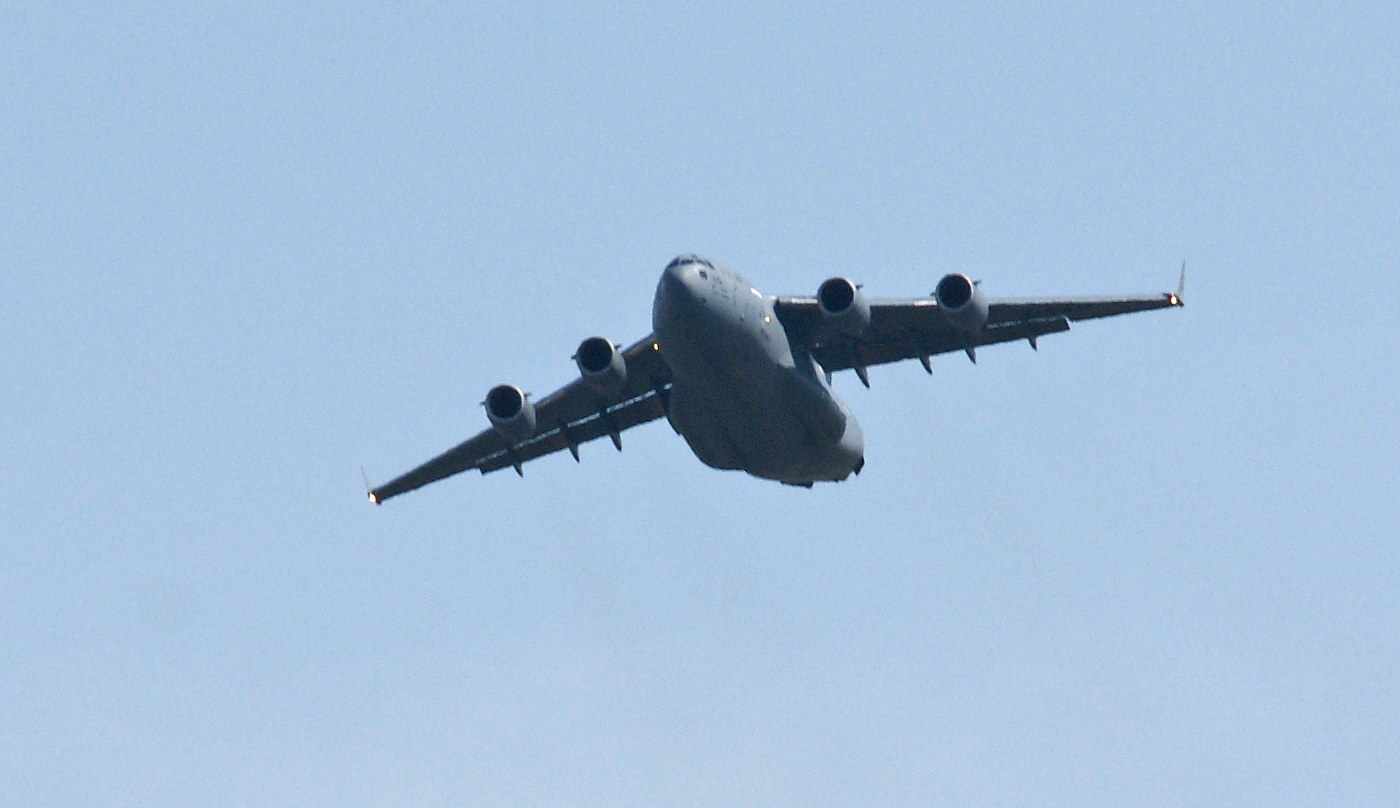
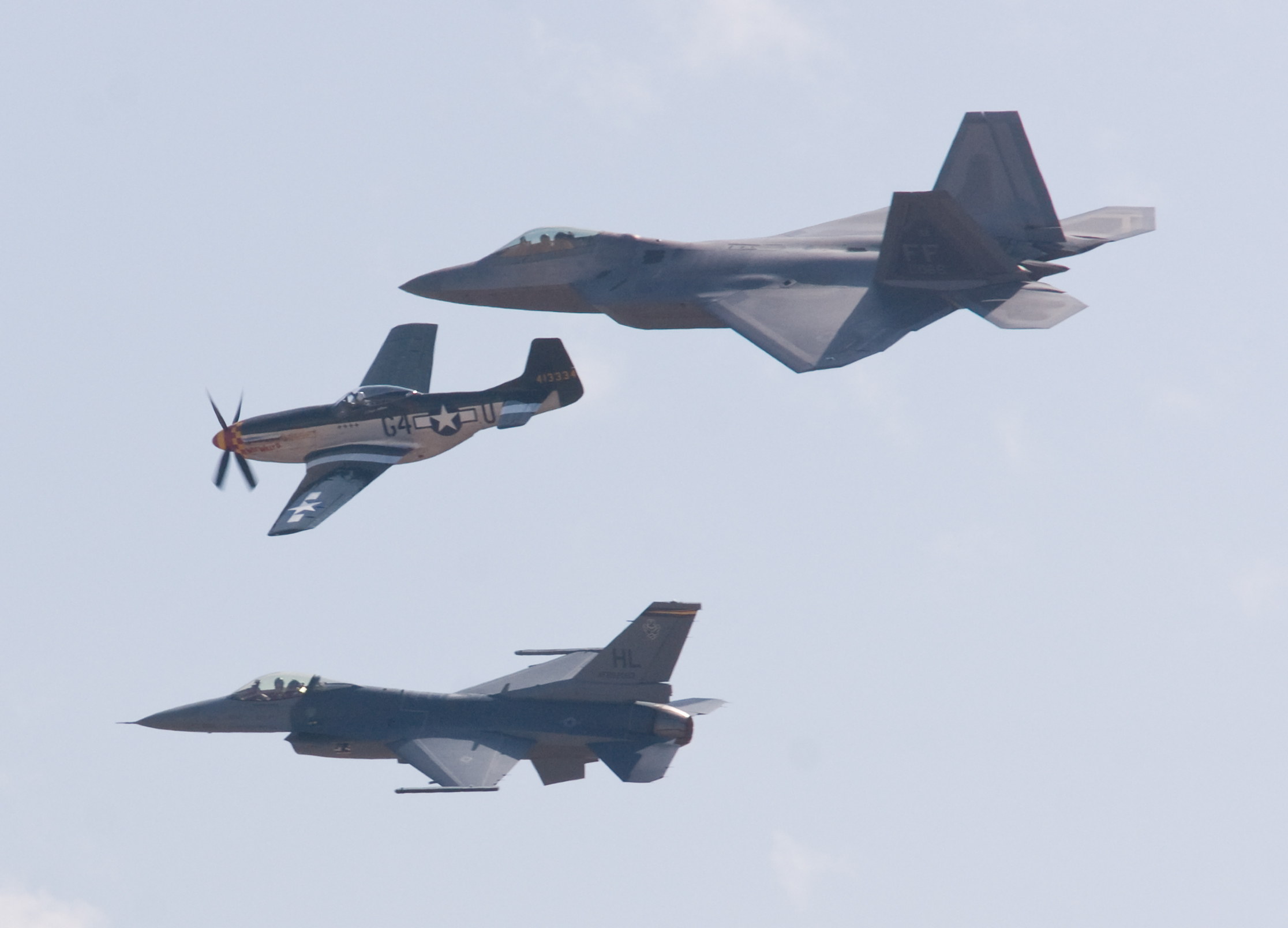
We love to travel and have acquired an interest in aircraft. Take a basic design — heck, we knew how to do that over 100 years ago — and twist it, compress it, stretch it, add extra engines, change the engine placement, and so on, and you create a testament to human ingenuity, creativity, engineering prowess, and most of all, to human dreams of flying.
We give them thrilling names like Starlifter, Mustang, Thunderbolt, Globemaster, and Invader, meant to inspire us. But we also name them Guppy, Gooneybird, and Aardvark, because flying is supposed to be fun. 😀
The Pima Air & Space Museum, one of the largest non-government funded aviation and space museums in the world, is located just outside of Tucson, Arizona. It is over 80 acres of aircraft, and we are here to see those flying machines.
Note: aircraft not to scale. But…we’re here!
There are more than 350 historical aircraft, some inside buildings and hangers, and some preserved in the dry Arizona air.
Note that we include a person in most of the photographs to give a scale of size.
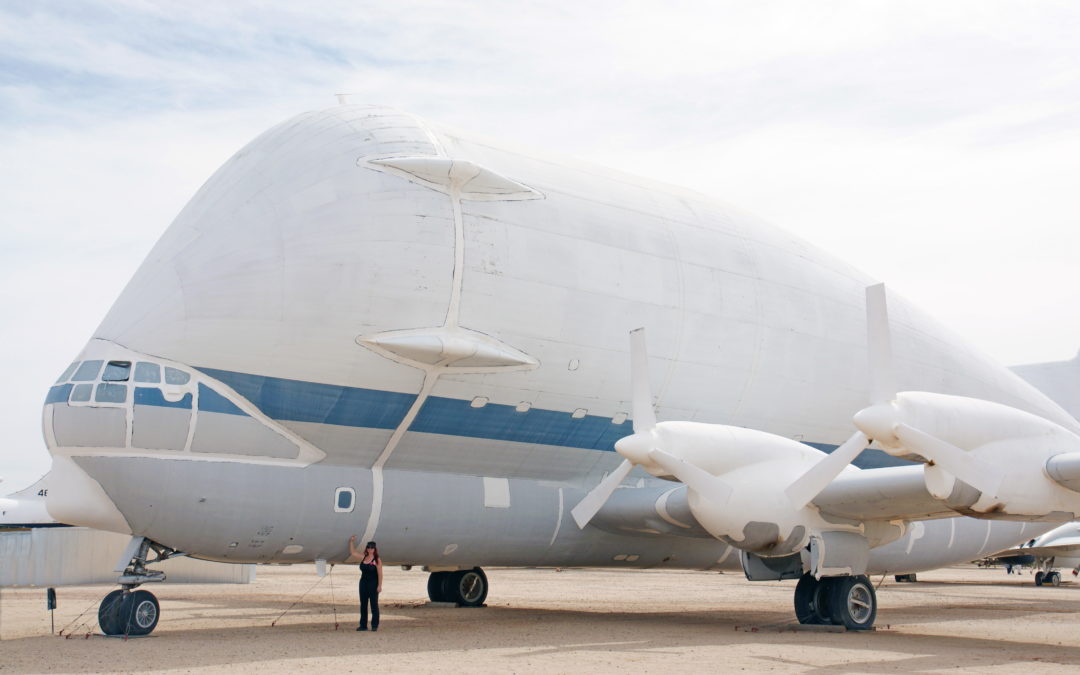
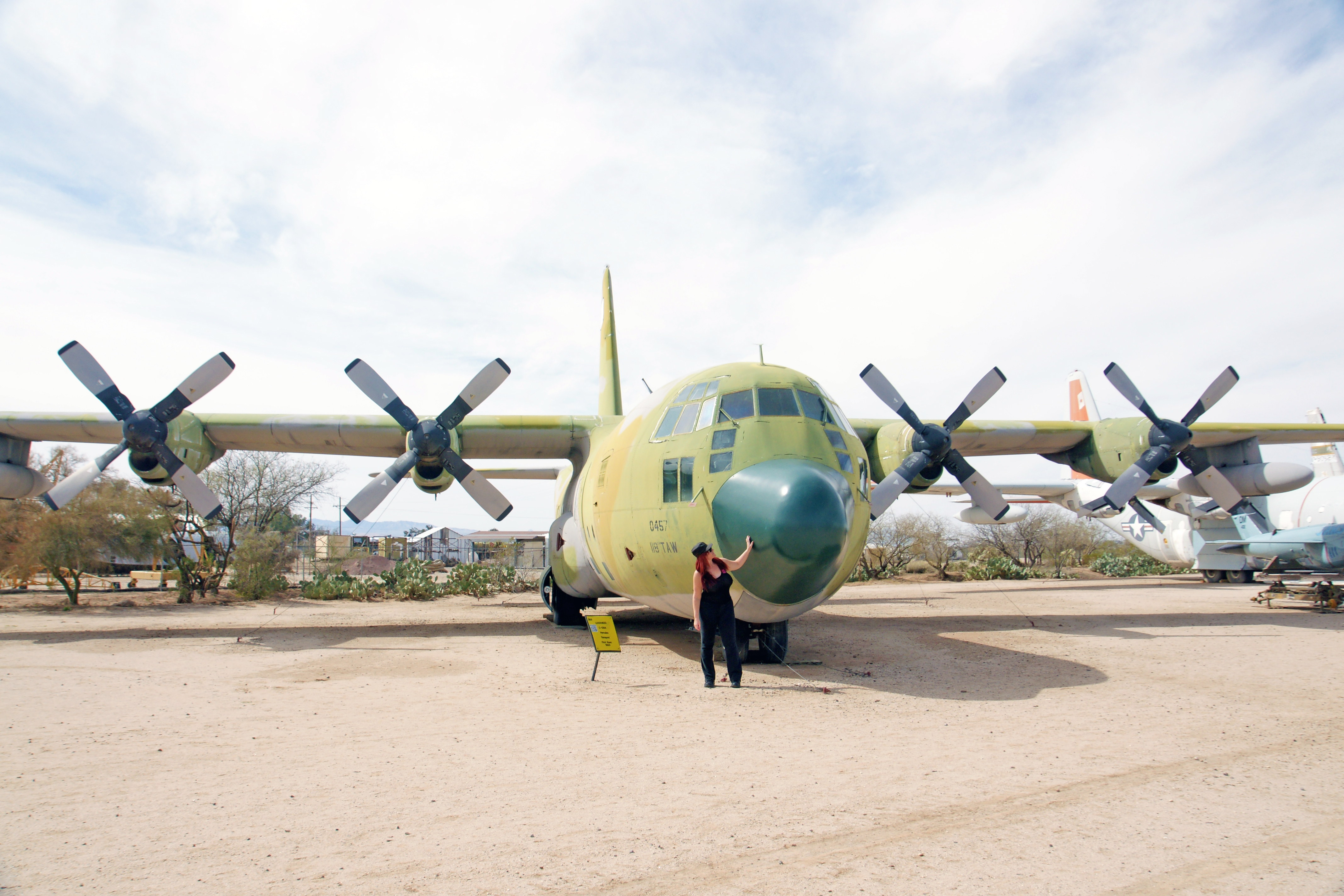
The Aero Spacelines Super Guppy can carry 54,000 pounds of cargo and cruise at 300 mph. To my eye, it looks like cgi from a bad sci-fi film, but these puppies, err, guppies, can really fly!
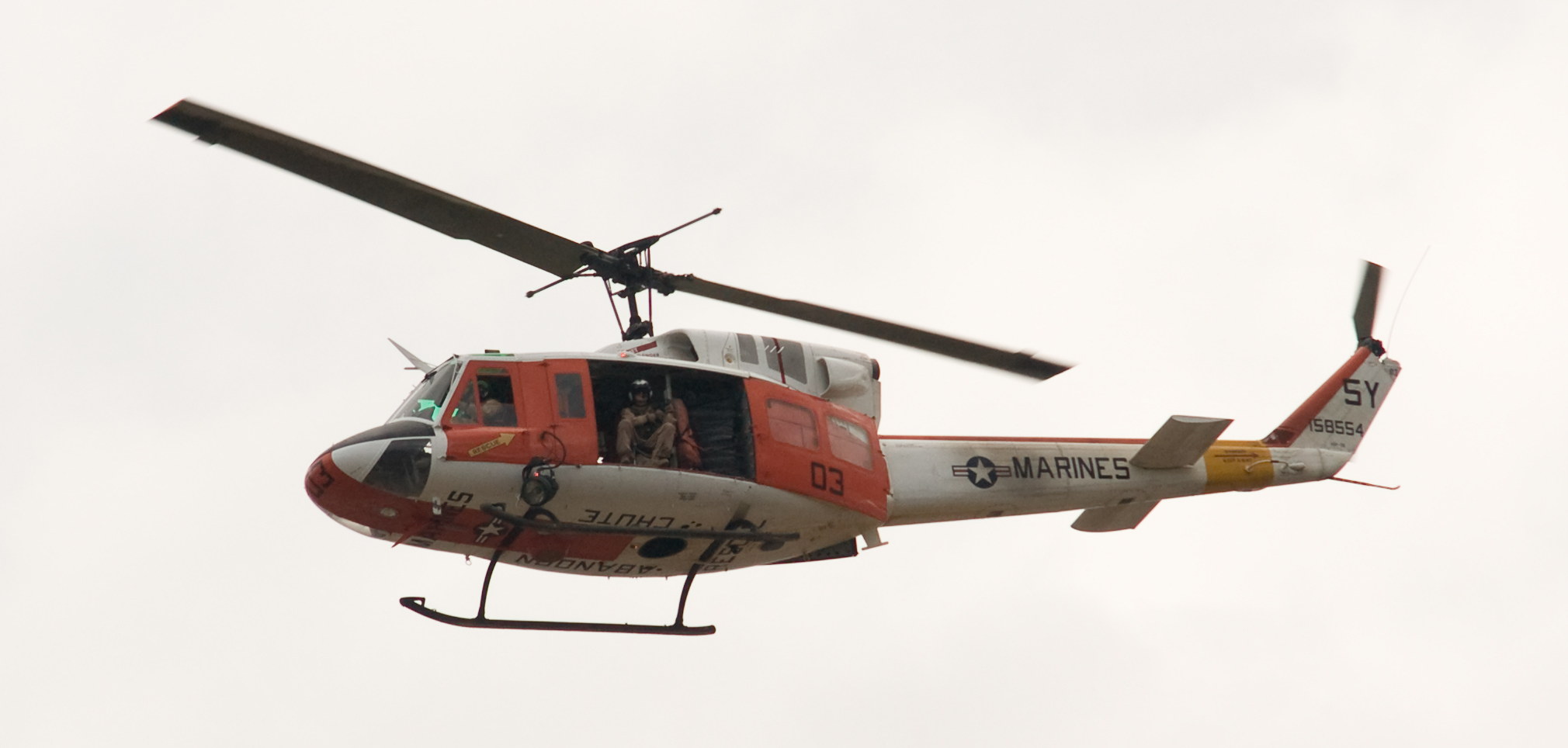
The Huey (nicknamed because it was originally designated “HU-1”) was first flown in 1956, and was the first turbine-powered helicopter used by the US military. More than 16,000 of them have been built, including two versions for the civilian market. There are quite a few more helicopters to be seen, all shapes and sizes.
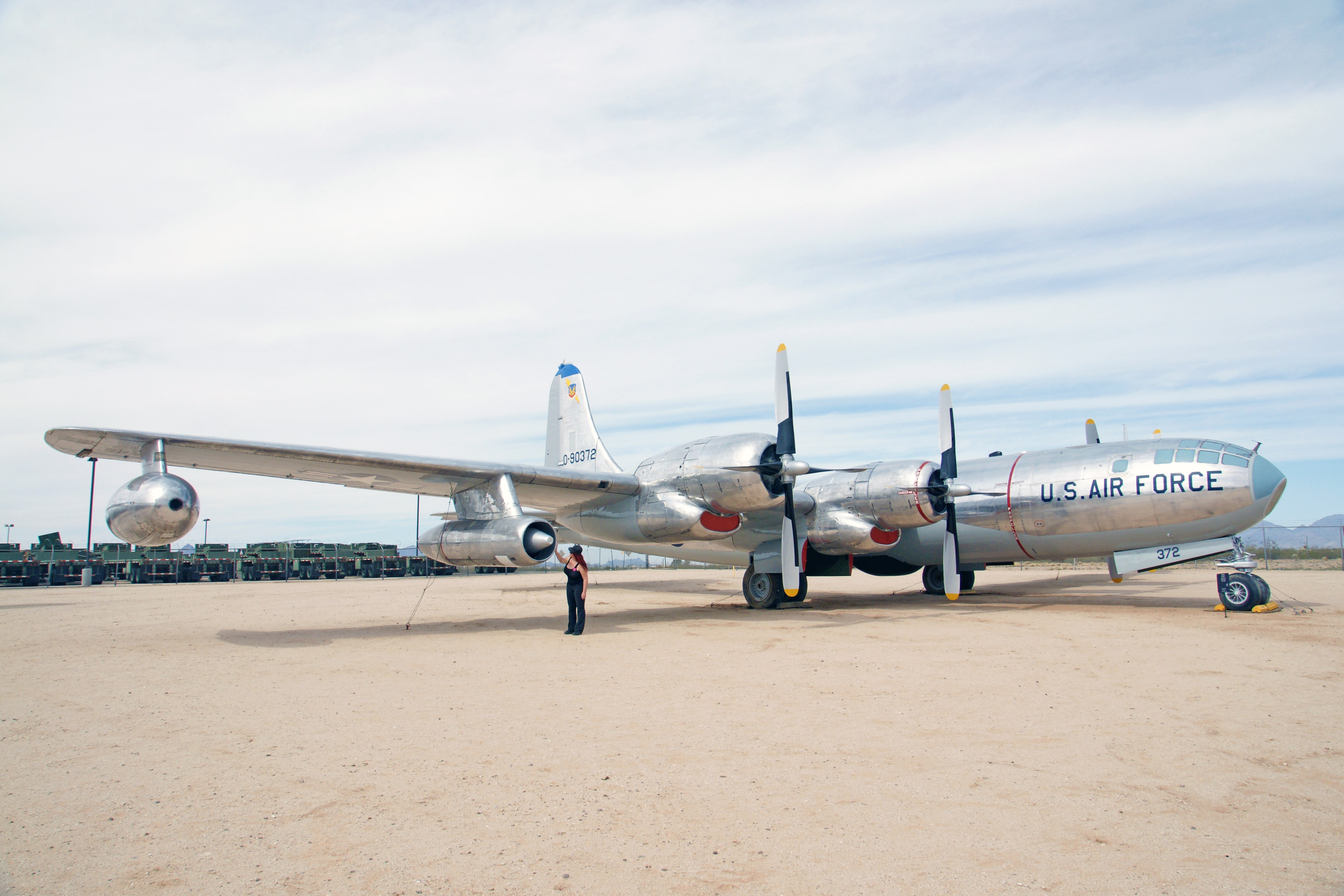
In movies, boys and men have a fascination with small, fast fighter planes. I confess that my preference is the big guys. The Superfortress was a strategic bomber used by the US Strategic Air Command, the Tactical Air Command, and the Air Weather Service (although probably not as a bomber). Boeing built 370 of the various B-50 models and variants between 1947 and 1953, the tanker and weather reconnaissance versions remaining in service until 1965. Notice the additional fuel tanks and probe-and-drogue equipment under the wing.
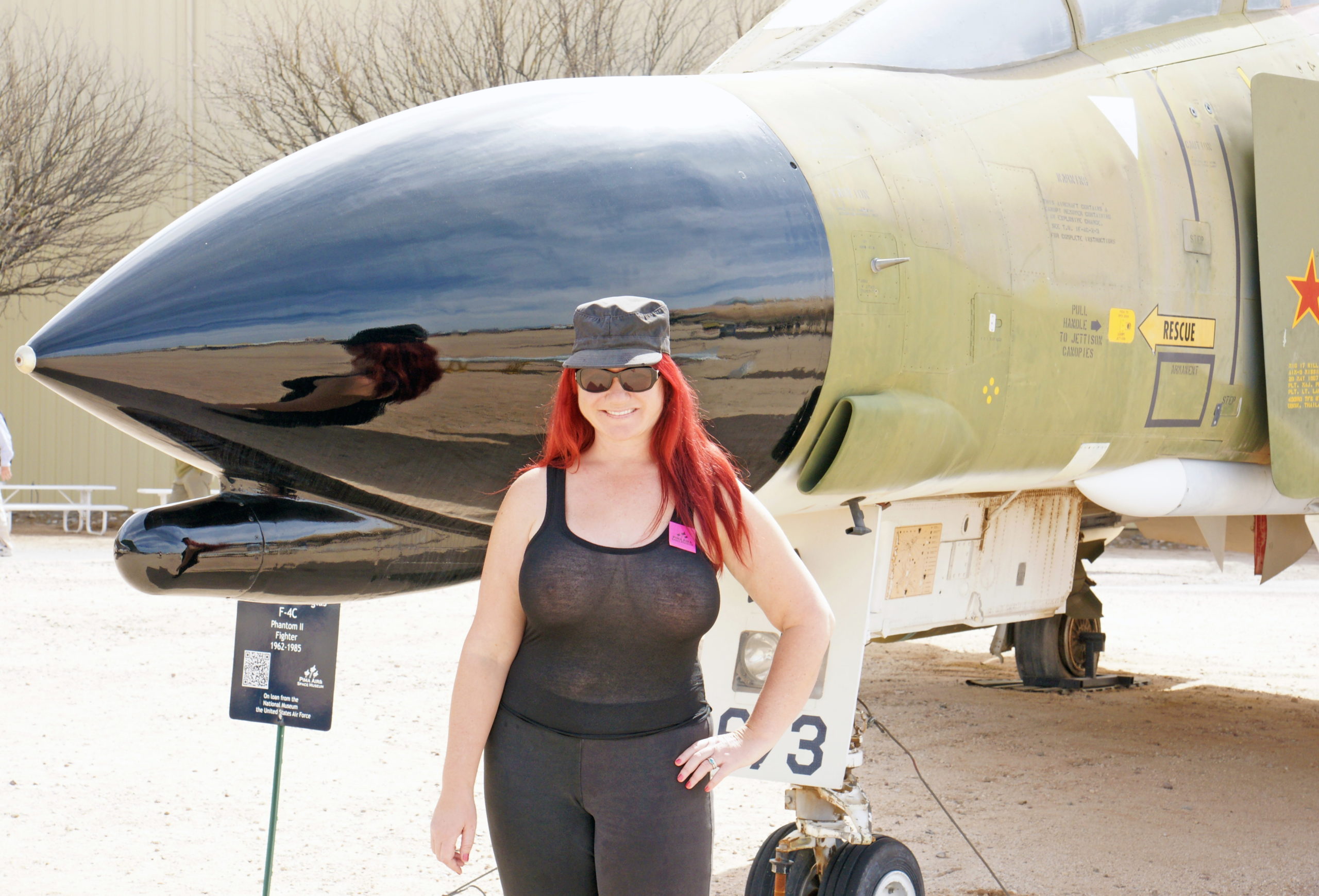
The McDonnell Douglas F 4 Phantom II was in service with the United States military from 1961 through 1996. It is currently in use by the military of Iran, South Korea, Greece, and Turkey. Question: why is part of the aircraft so shiny that it can be used as a mirror? Isn’t that the opposite of good?
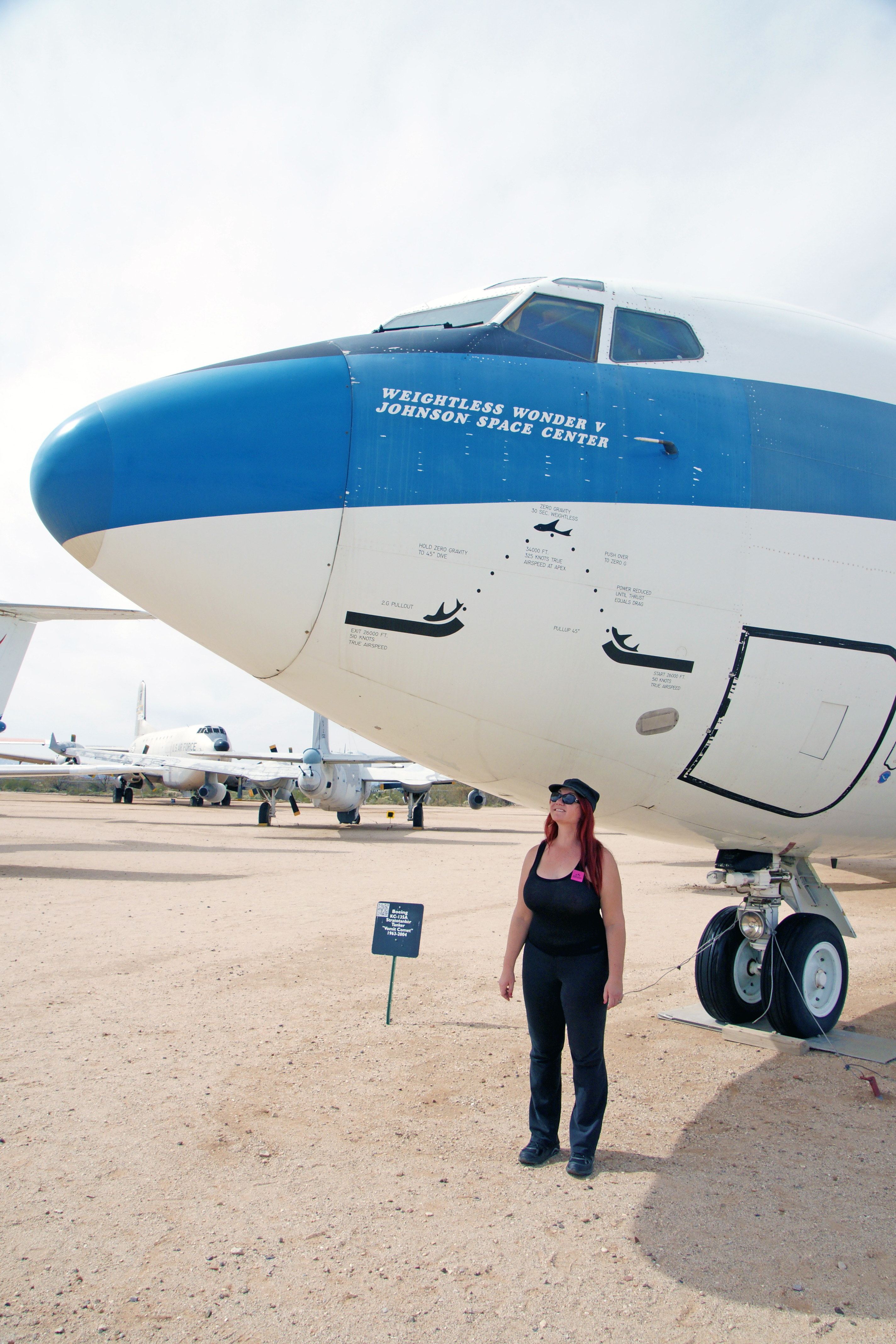
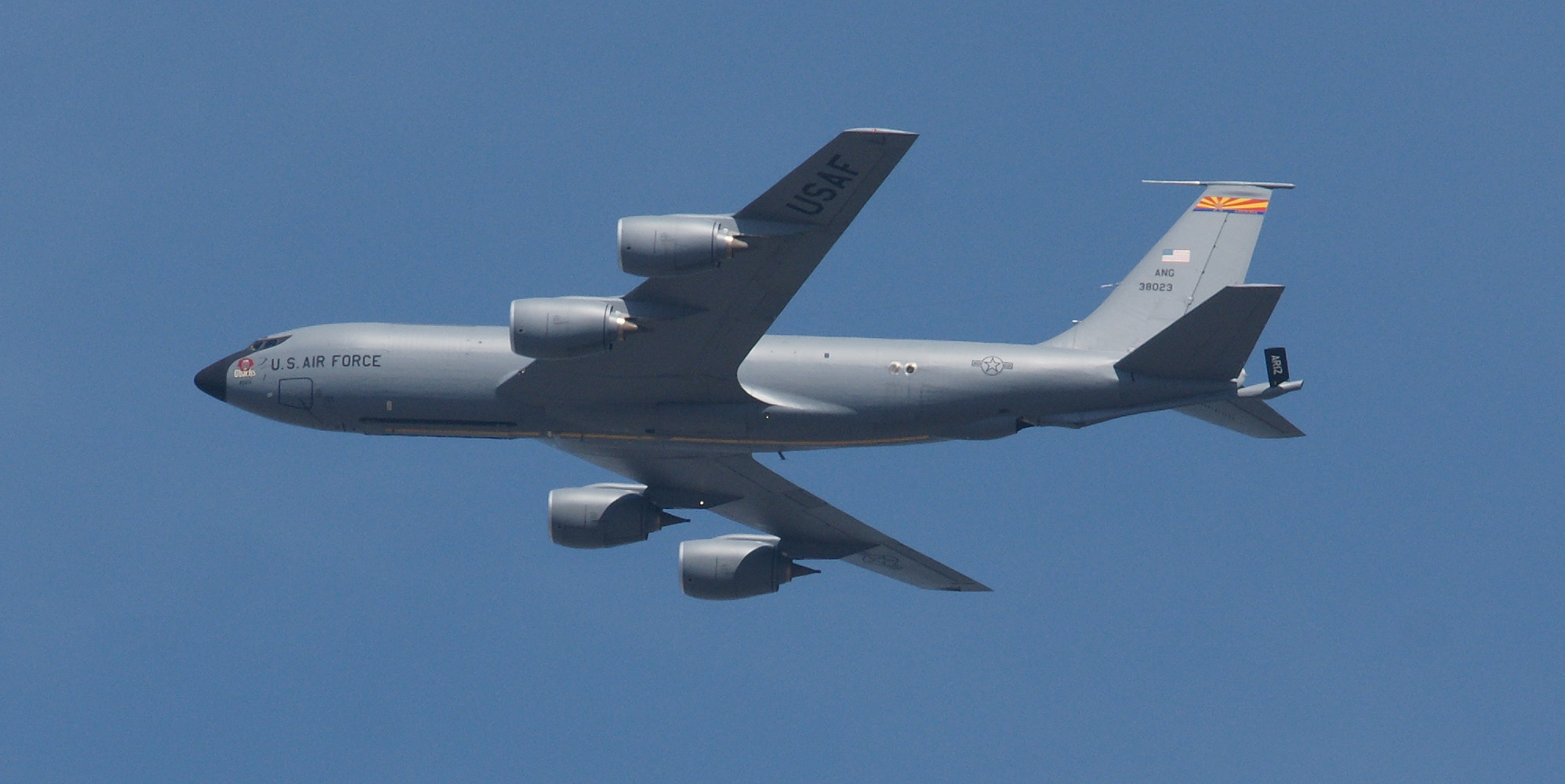
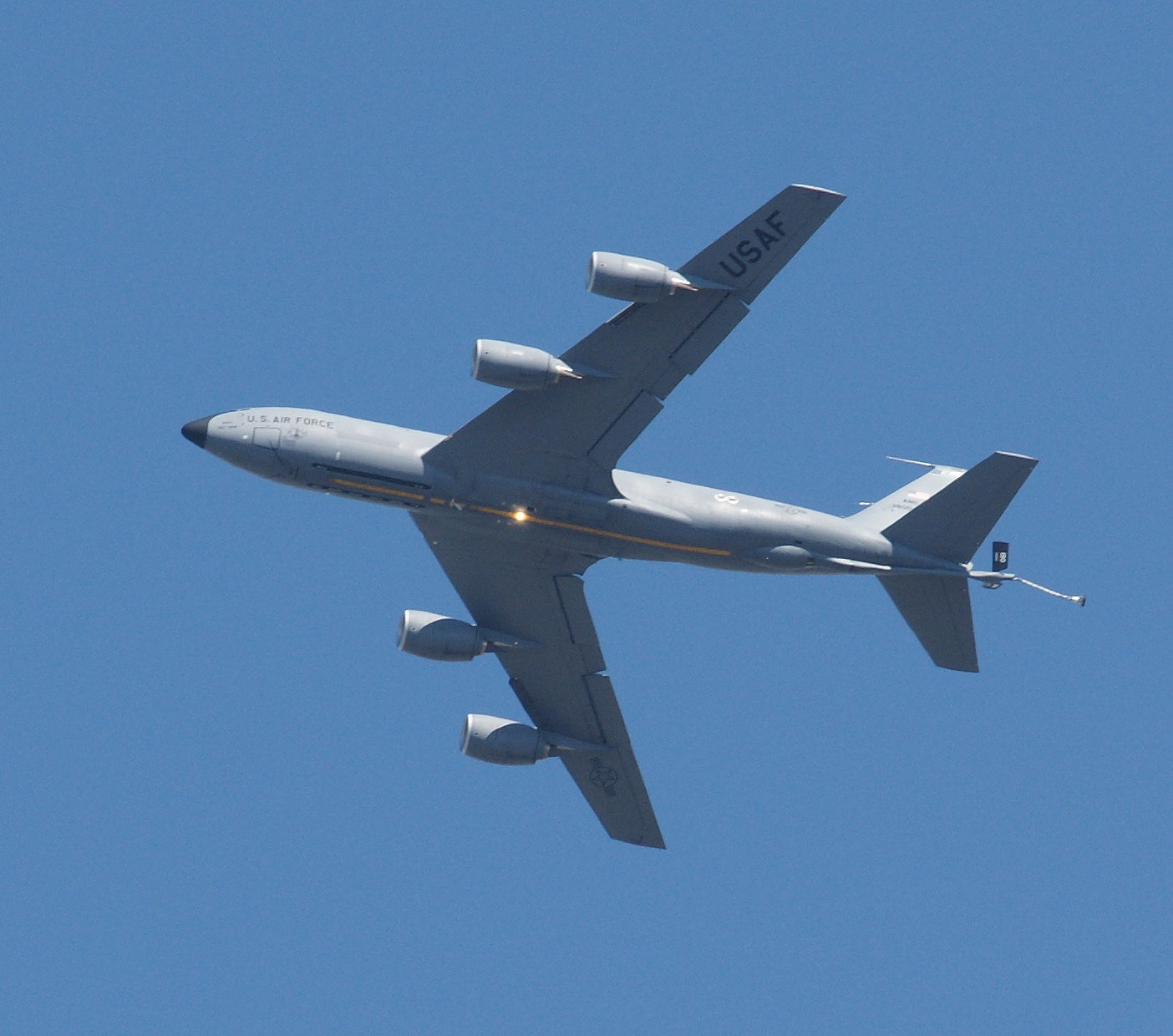
The Stratotanker was designed a refueling aircraft. However, the Vomit Comet, a reduced-gravity aircraft, serves a different purpose: it simulates zero-gravity spaceflight by descending at the speed of gravity such that passengers are “falling” while enclosed in the safety of the aircraft.
Sadly, this aircraft has been retired. I hope/expect our children’s children will travel though space as casually as we travel through the air, and this marvelous aircraft will remind them of humanities’ pioneering spirit.
This stratofreighter was employed as a strategic tanker aircraft (notice the probe-and-drogue equipment under the wing). The cavernous upper deck was capable of accommodating oversize cargo accessed through a very large right-side door. In addition, transferrable jet fuel was contained in tanks on the lower deck (G-L models). Both decks were heated and pressurized for high altitude operations.
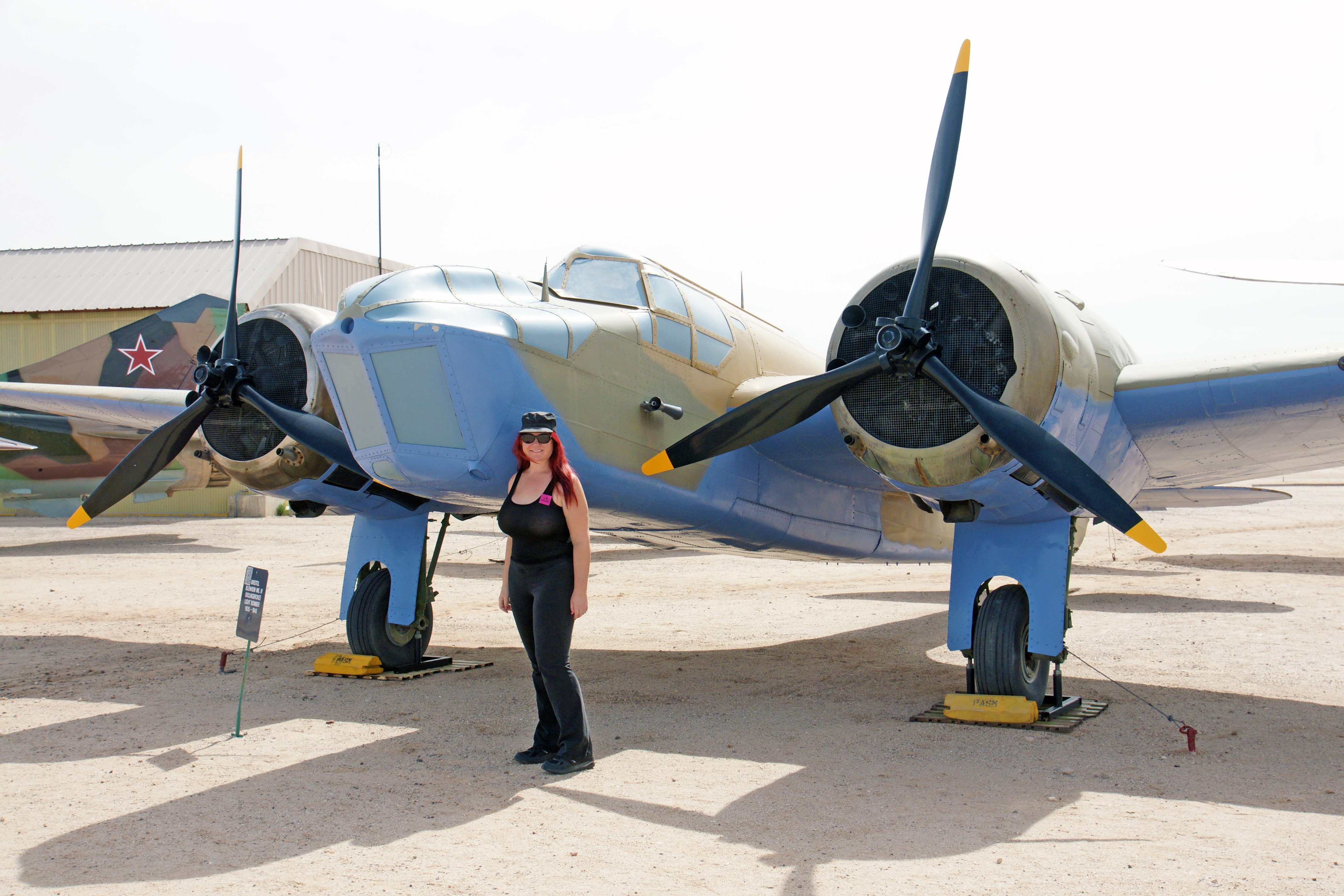
The Bristol Fairchild Bolingbroke was a maritime patrol aircraft used by the Royal Canadian Air Force during the Second World War. Development of the Blenheim began in 1935 as a development of a civil transport. When it first appeared, the Blenheim was faster than most of the fighters then in use by the Royal Canadian Air Force, but by the outbreak of war in 1939 it was slow and nearly obsolete. Nevertheless, it served extensively in the first three years of the war as a bomber, night-fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft. A version of the Blenheim Mk. IV was built in Canada by Fairchild called the Bolingbroke. These aircraft served primarily as coastal patrol planes and as trainers.
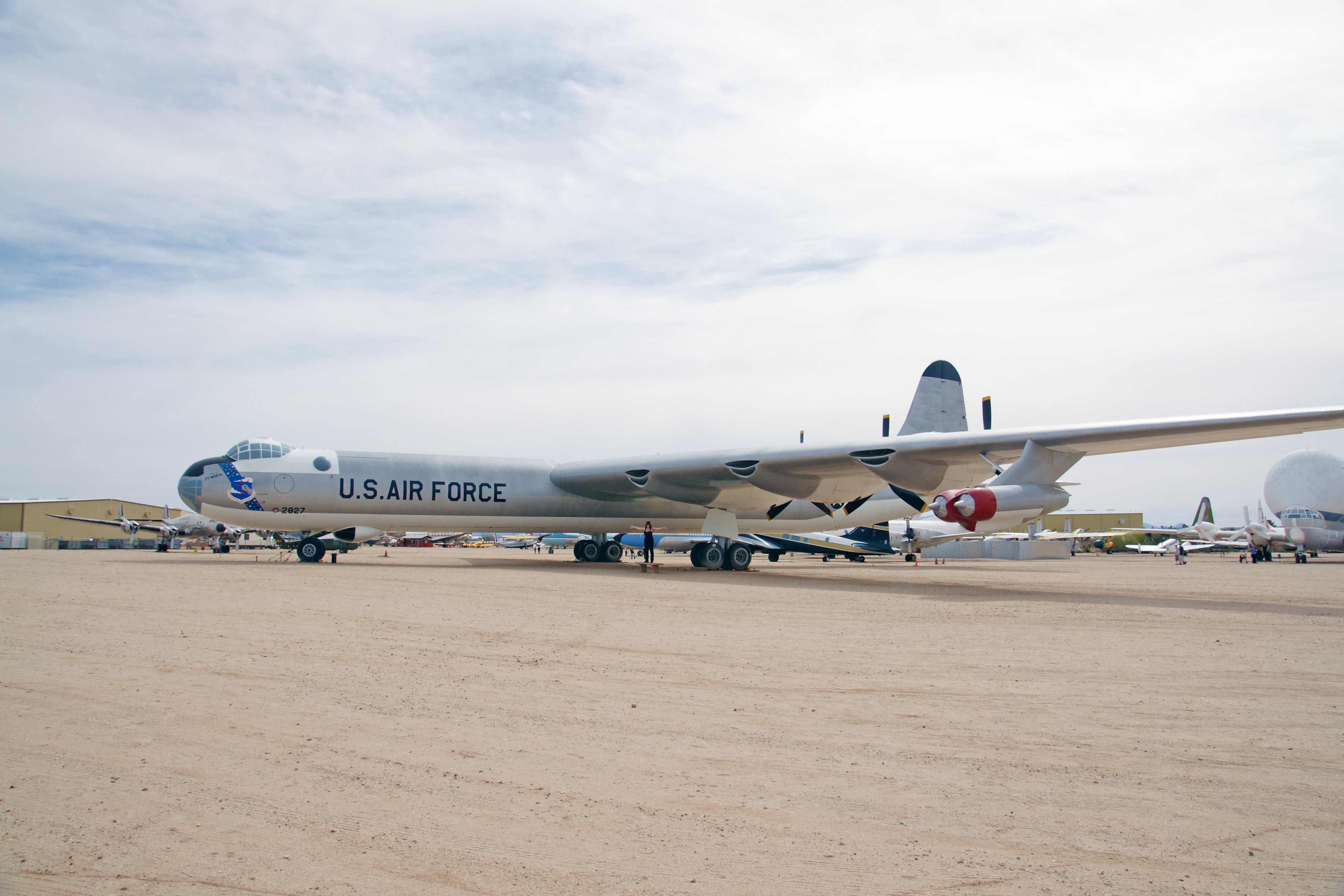
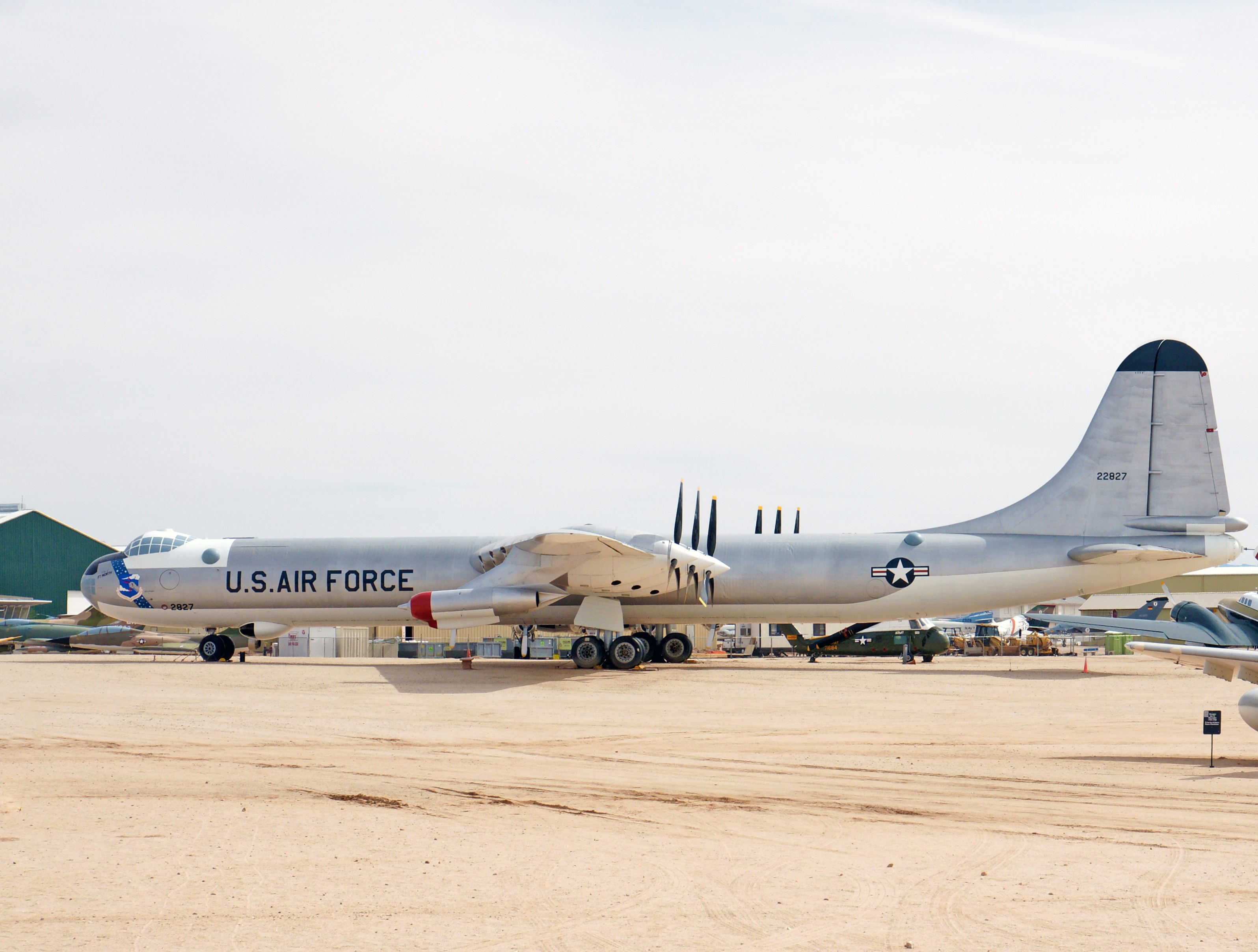
The Peacemaker was the largest mass-produced piston-engine aircraft ever built, and the longest wingspan (230 feet) of any combat aircraft ever built. The B-36 was the first bomber capable of delivering any of the nuclear weapons in the U.S. arsenal from inside its four bomb bays without aircraft modifications. With a range of 10,000 miles and a maximum payload of 87,200 pounds, the B-36 was capable of intercontinental flight without refueling. Notice the additional 4 jet engines mounted on the wingtips
The Peacemaker is 162 feet long.
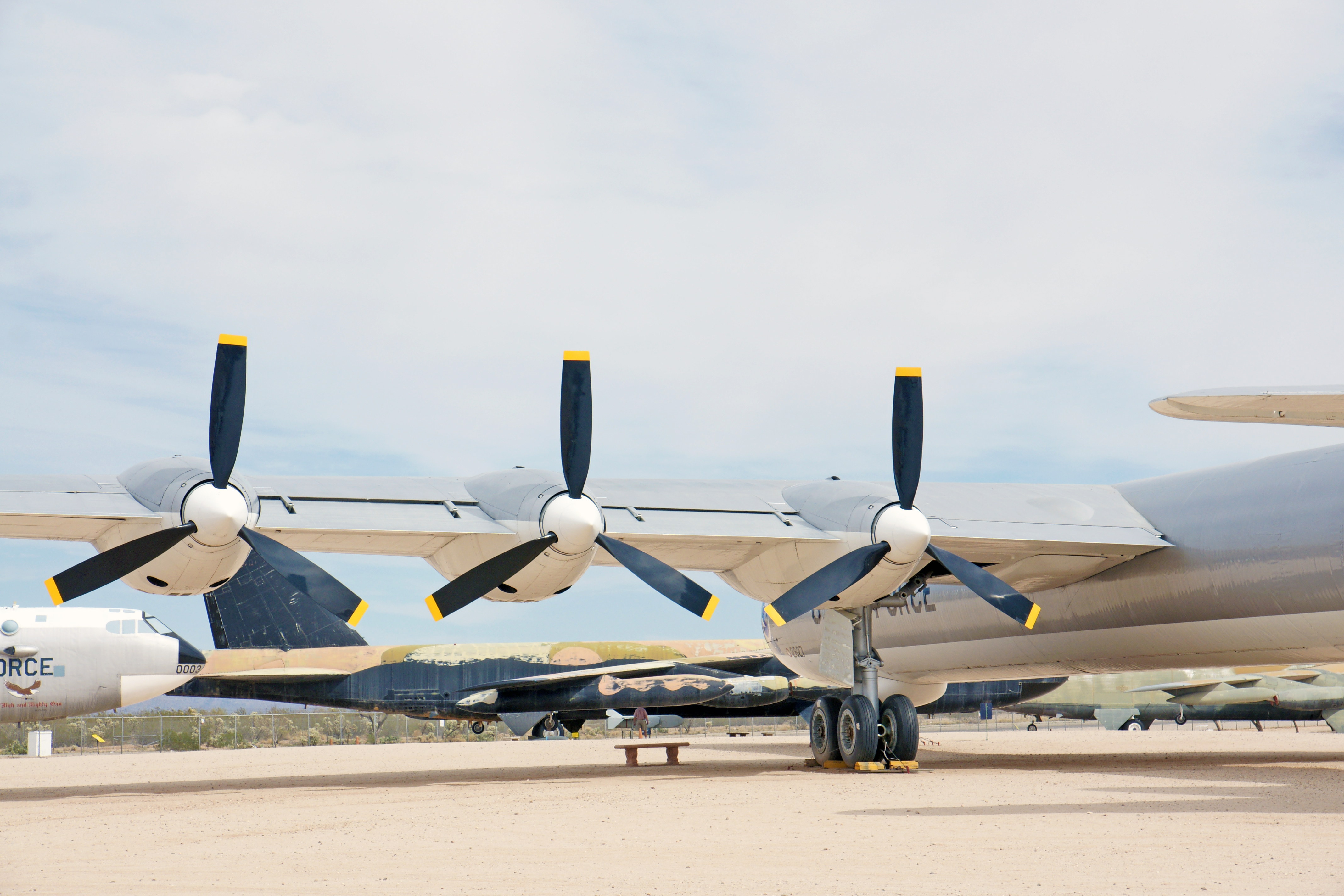
The propellers of the Peacemaker are in a pusher configuration, with six 3,800 hp Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major radial engines mounted in the wing, each driving a pusher propeller located behind the trailing edge of the wing.
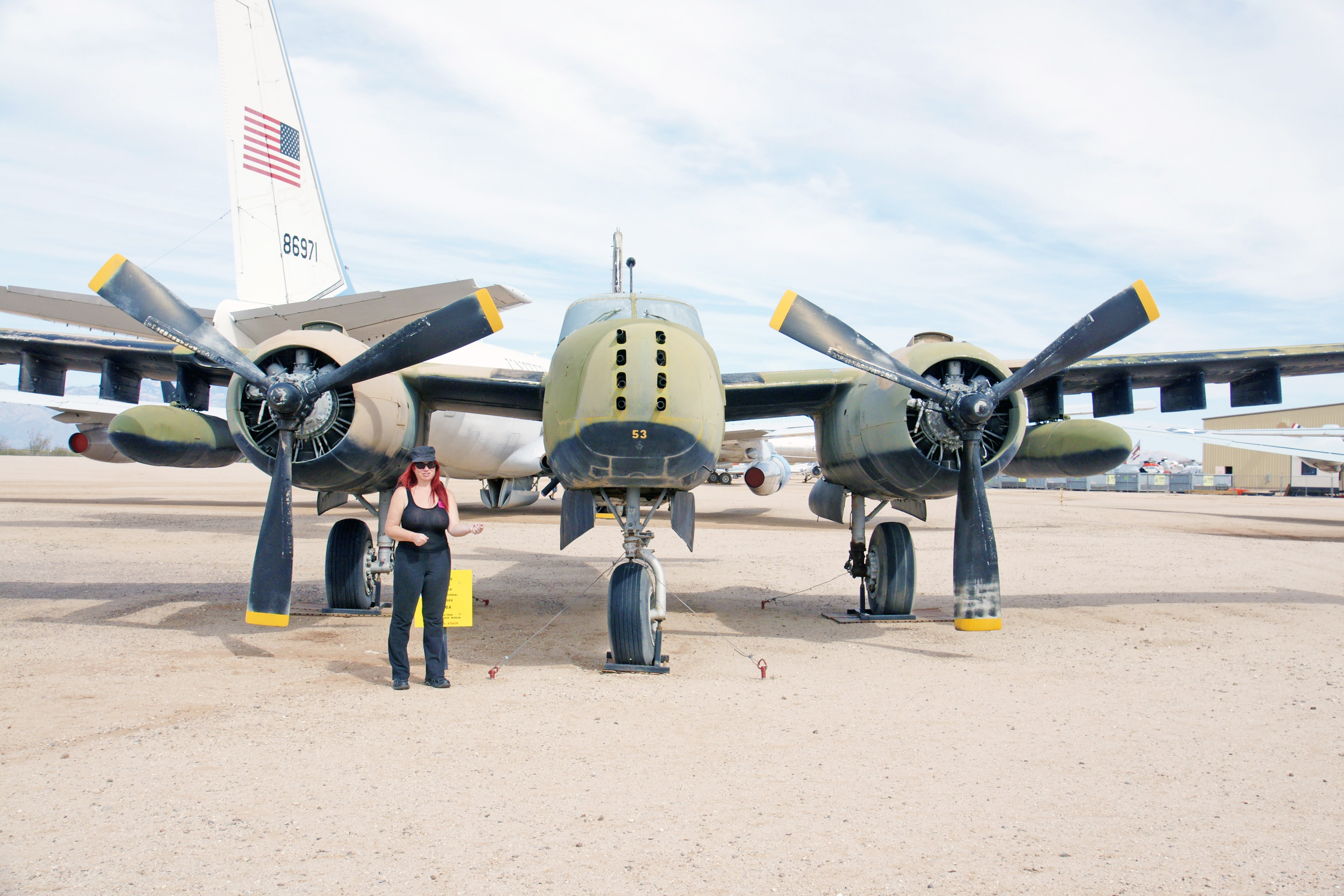
The Douglas Invader is a light bomber and ground attack aircraft. The variant shown here had an “eight-gun nose”, each gun a .50 caliber machine gun. The Invader was in service from 1948 to 1965, most notoriously by the US Central Intelligence Agency in the Bay of Pigs Invasion.
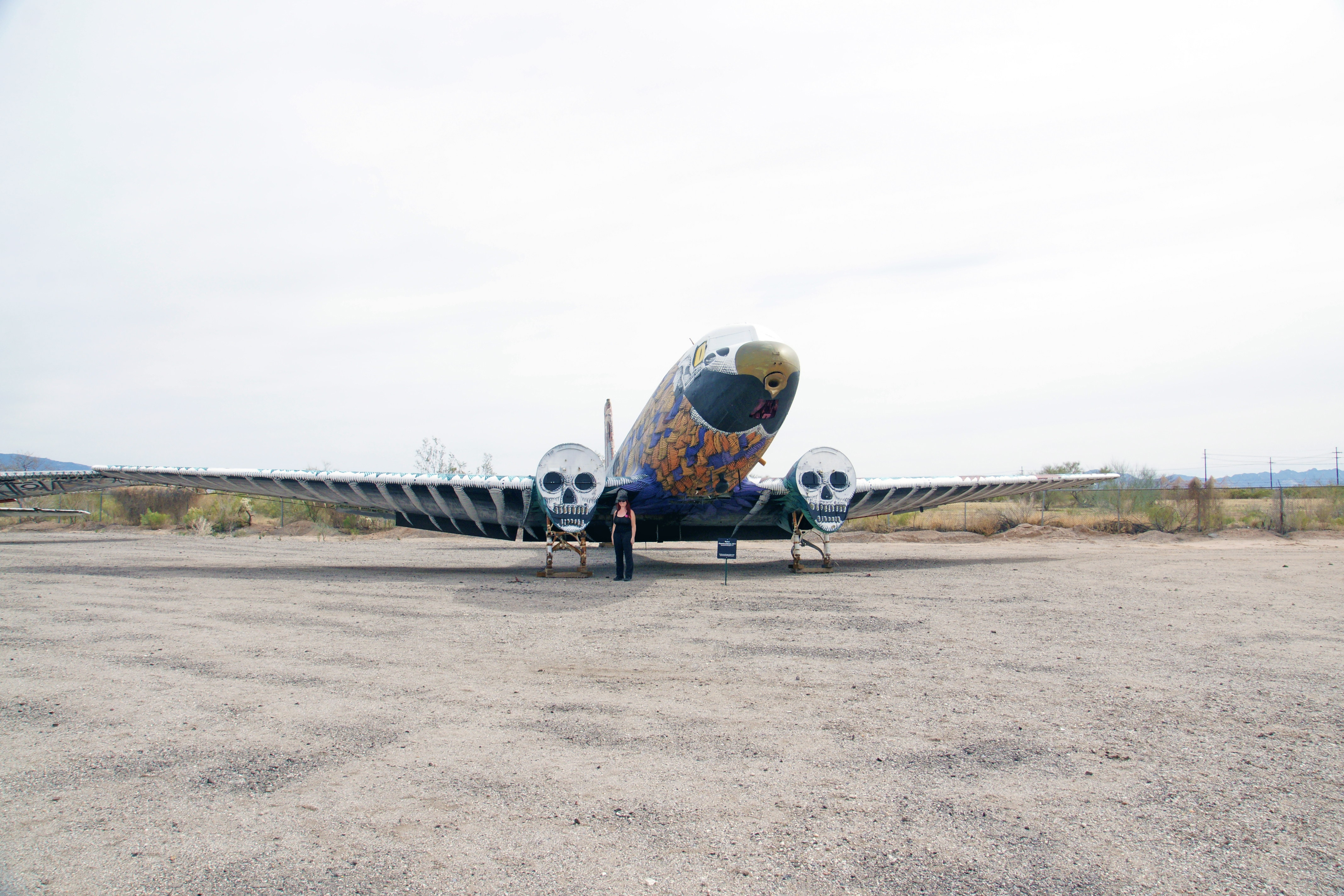
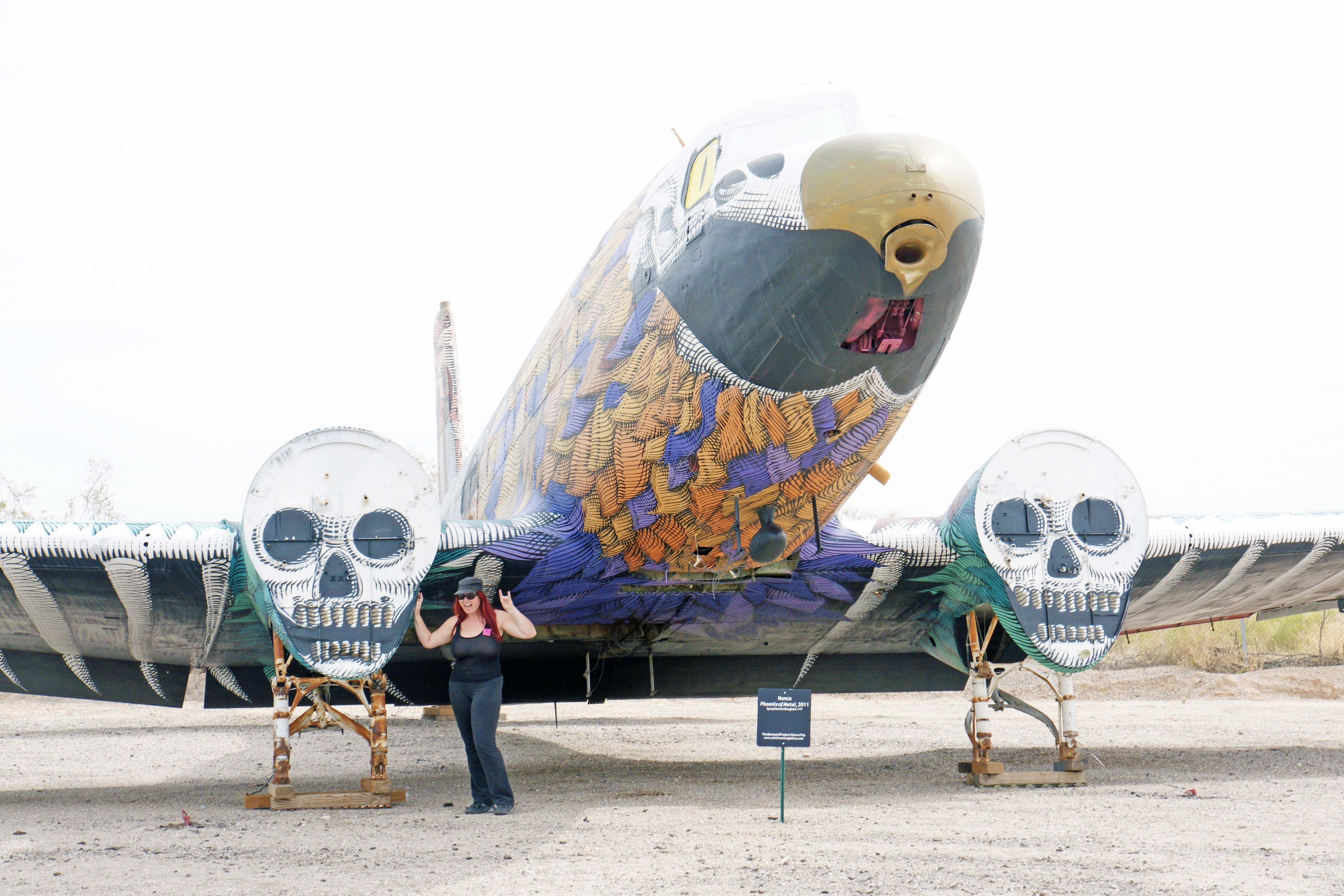
The C-117 was based on the reliable and proven DC-3/C-47 and was originally intended for the civilian airline market. The “Super DC-3” featured a longer fuselage, redesigned tail and wings, and fully enclosed the landing gear when retracted. In 1951 the Navy evaluated the Super DC-3 and liked the increased performance and accepted the aircraft as the R4D-8. Rather than purchase new aircraft a total of 98 earlier R4Ds were converted to R4D-8 standards. In 1962, the R4D-8 was re-designated under the joint Air Force-Navy designation system as the C-117D. Super Gooney Birds continued in U.S. Navy service into the mid-1970s
The decoration on this aircraft was done with spray paint on a Douglas C-117 by Nunca in 2011 and named ‘Phoenix of Metal.
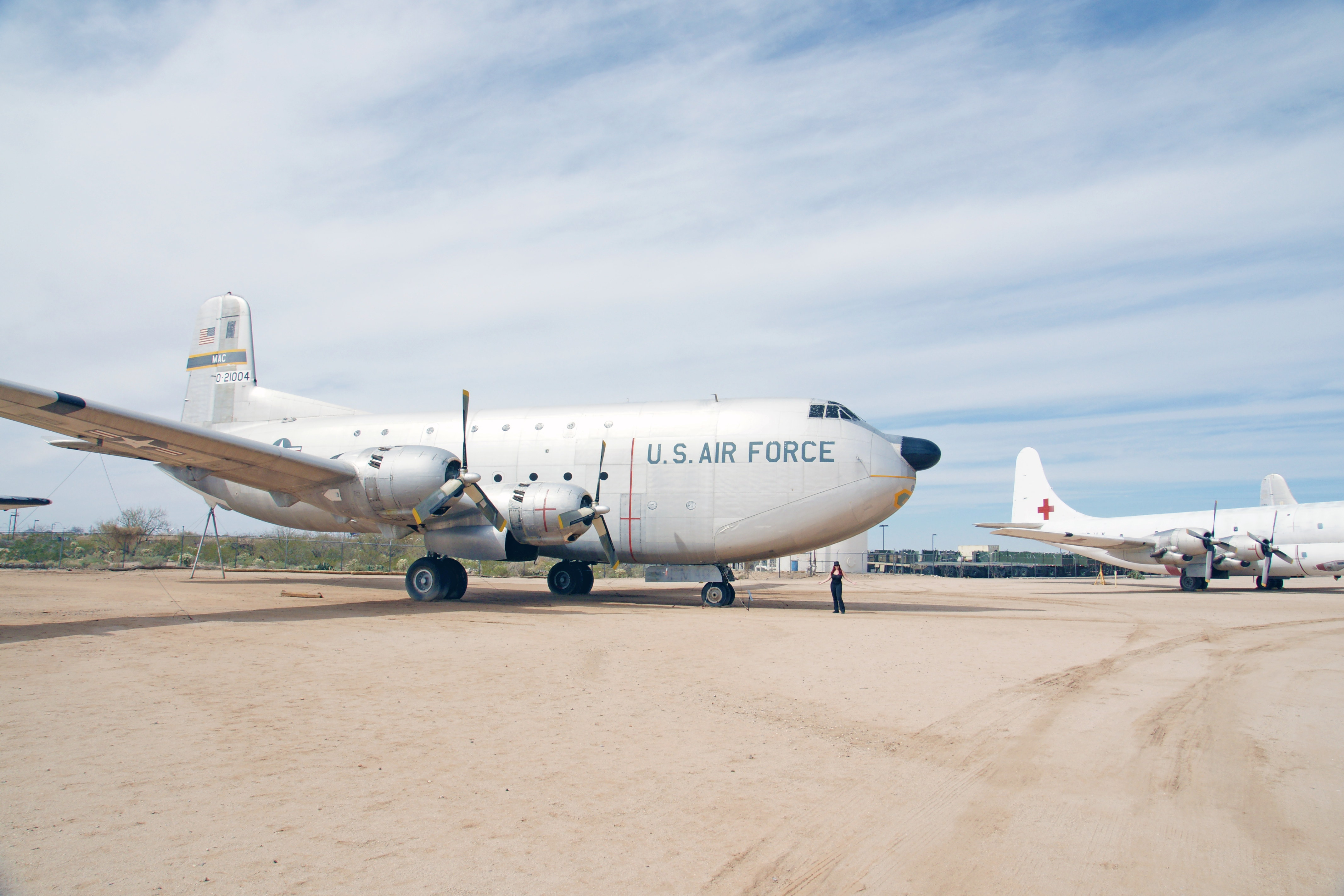
C-124 Globemasters provided resupply missions to Antarctica, refugee evacuation in the Congo and mercy flights to Morocco, Chile and elsewhere throughout the world following floods and other natural disasters, in addition to heavy airlift during the Korean War and the Southeast Asia War. The U.S. Air Force bought 448 C-124s before production ended in 1955.
To facilitate cargo handling, the C-124, or “Old Shakey” as it was affectionately known, featured “clamshell” loading doors and hydraulic ramps in the nose and an elevator under the aft fuselage. It was capable of handling such bulky cargo as tanks, field guns, bulldozers and trucks. It could also be converted into a transport capable of carrying 200 fully-equipped soldiers or 127 litter patients and their attendants in its double-decked cabin.
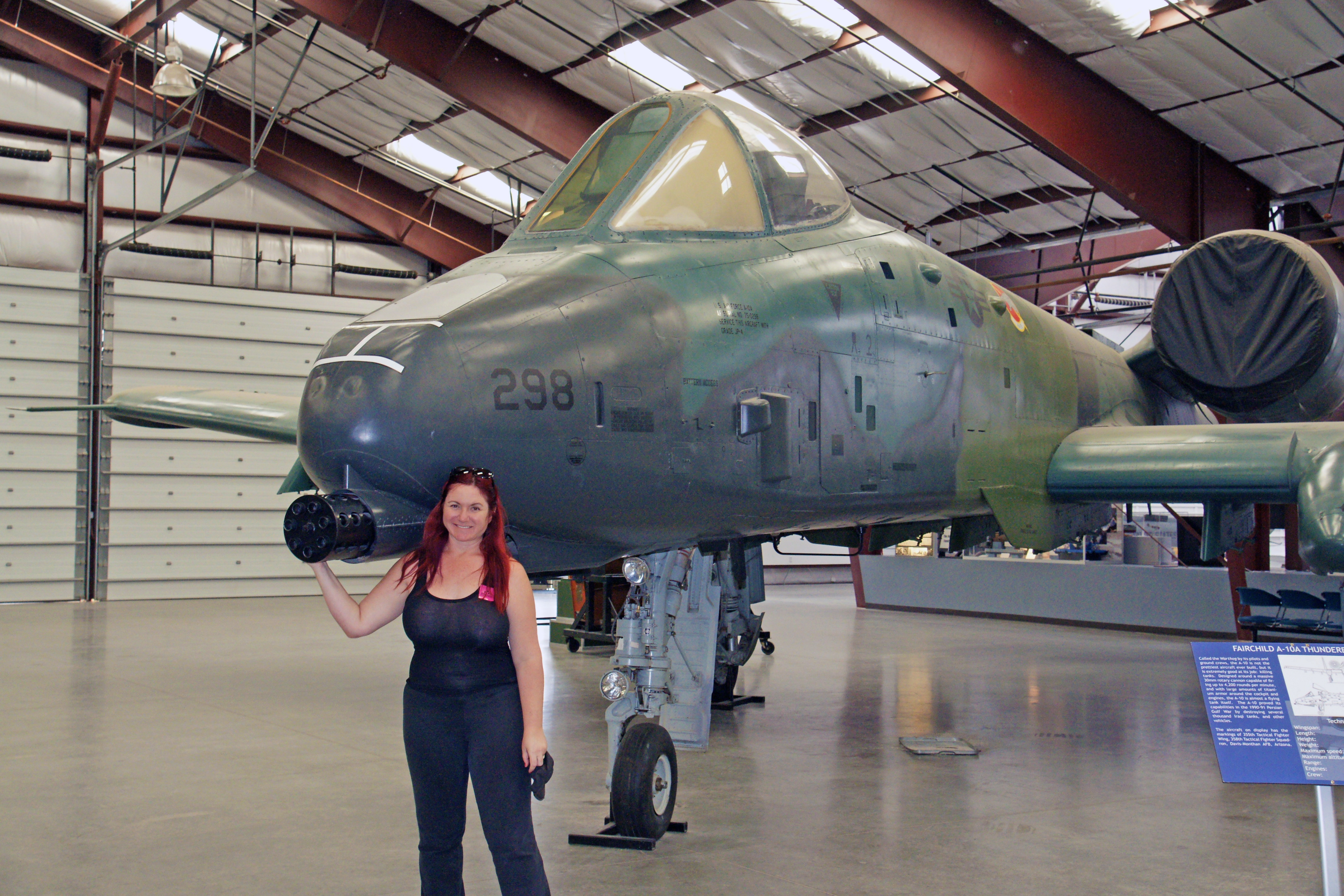
The Thunderbolt, aka Warthog, is the only production-built aircraft that has served in the USAF that was designed solely for close air support. It was designed around the 30 mm GAU-8 Avenger rotary cannon which fires depleted uranium armor-piercing shells at 3,900 rounds per minute, or 65 per second. The aircraft has 1,200 pounds of titanium armor protecting the cockpit and avionics. We have seen these flying near airbases in southern California; their distinctive shape makes them instantly recognizable.
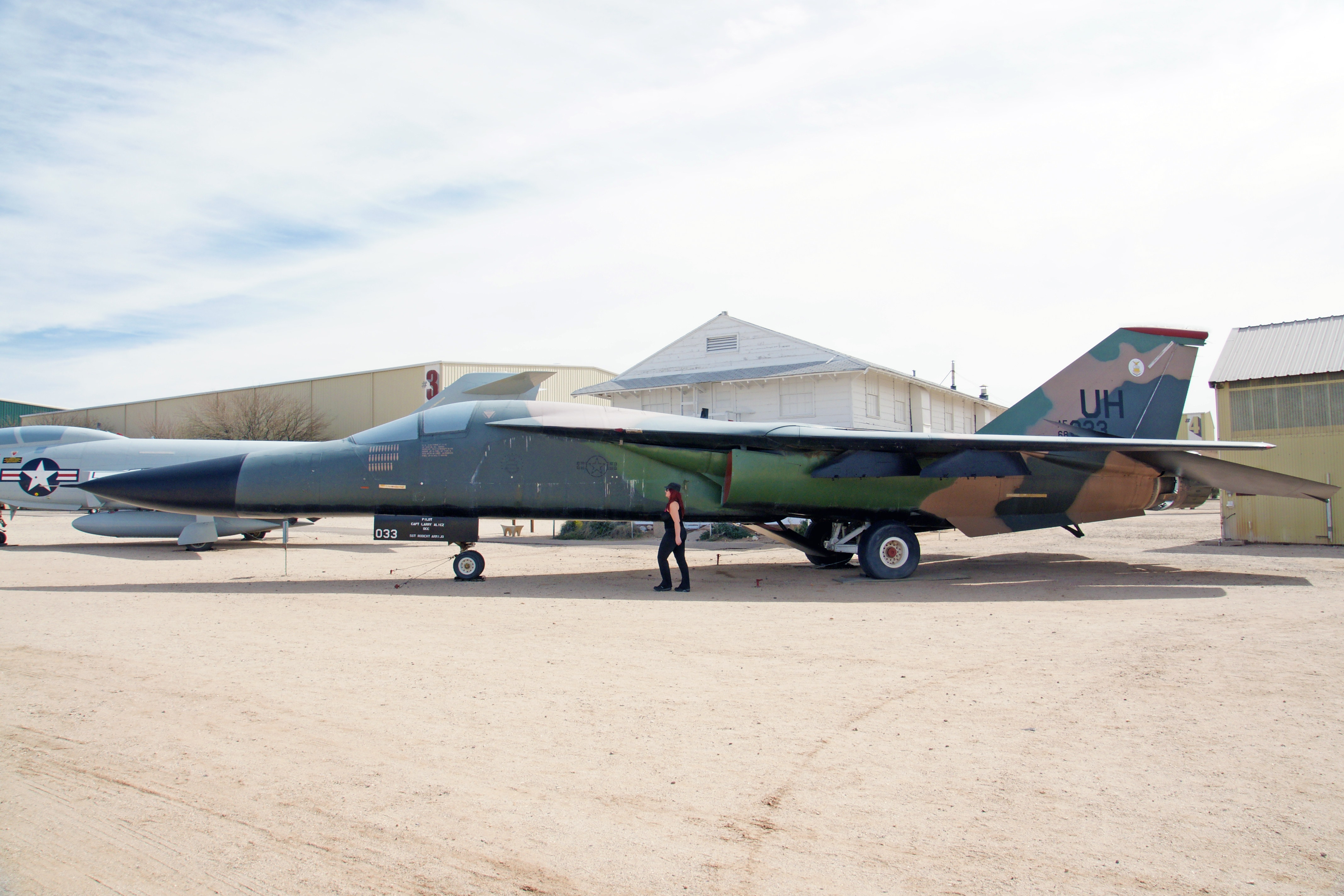
The Aardvark was a supersonic, medium-range interdictor and tactical attack aircraft that also filled the roles of strategic nuclear bomber, aerial reconnaissance, and electronic-warfare aircraft in its various versions. (Hint: supersonic aircraft have needle-noses; subsonic do not.) This was an all-weather attack aircraft, capable of low-level penetration of enemy defenses, featured variable-geometry wings, an internal weapons bay and a cockpit with side-by-side seating. The F-111 was the first production variable-geometry wing aircraft.
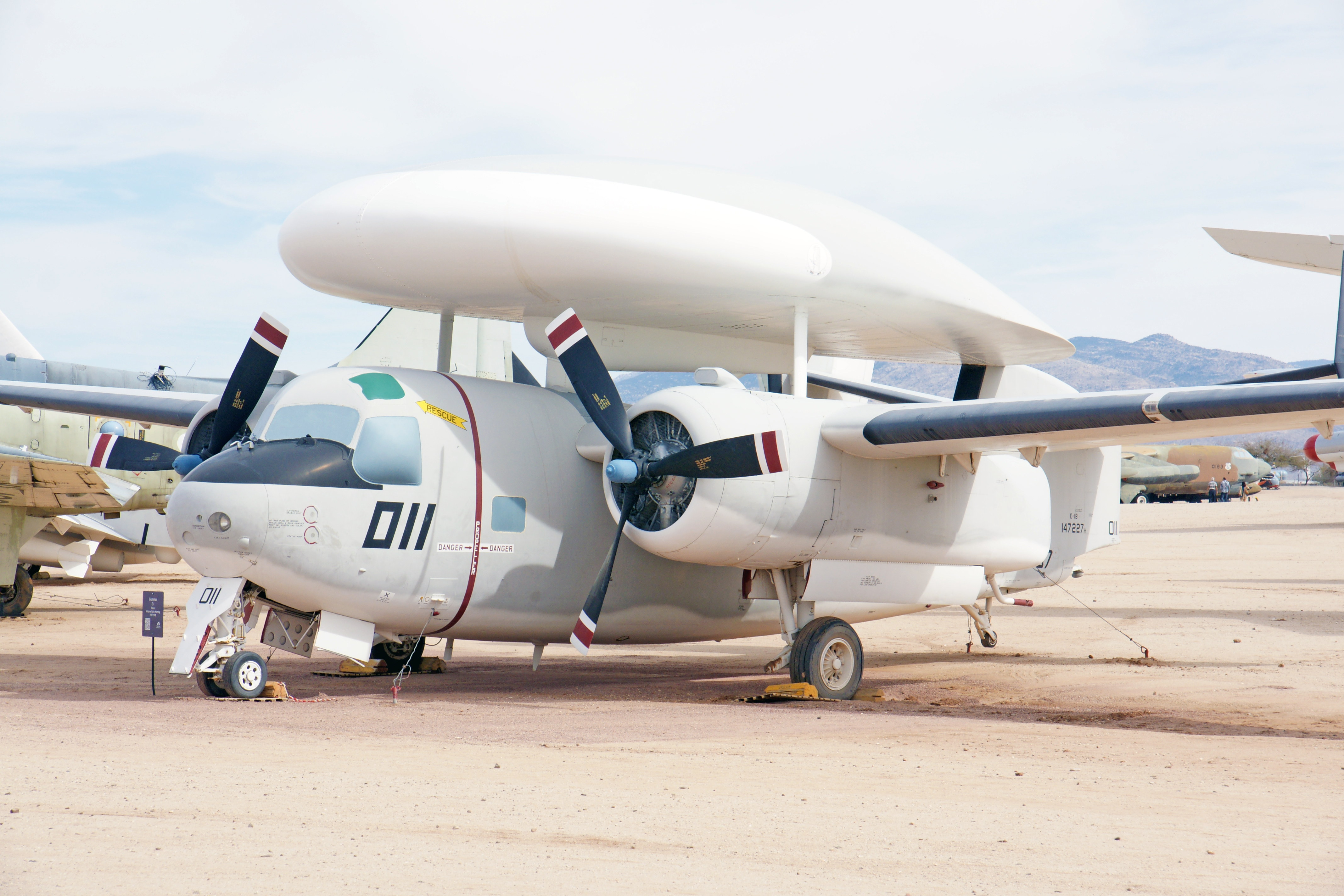
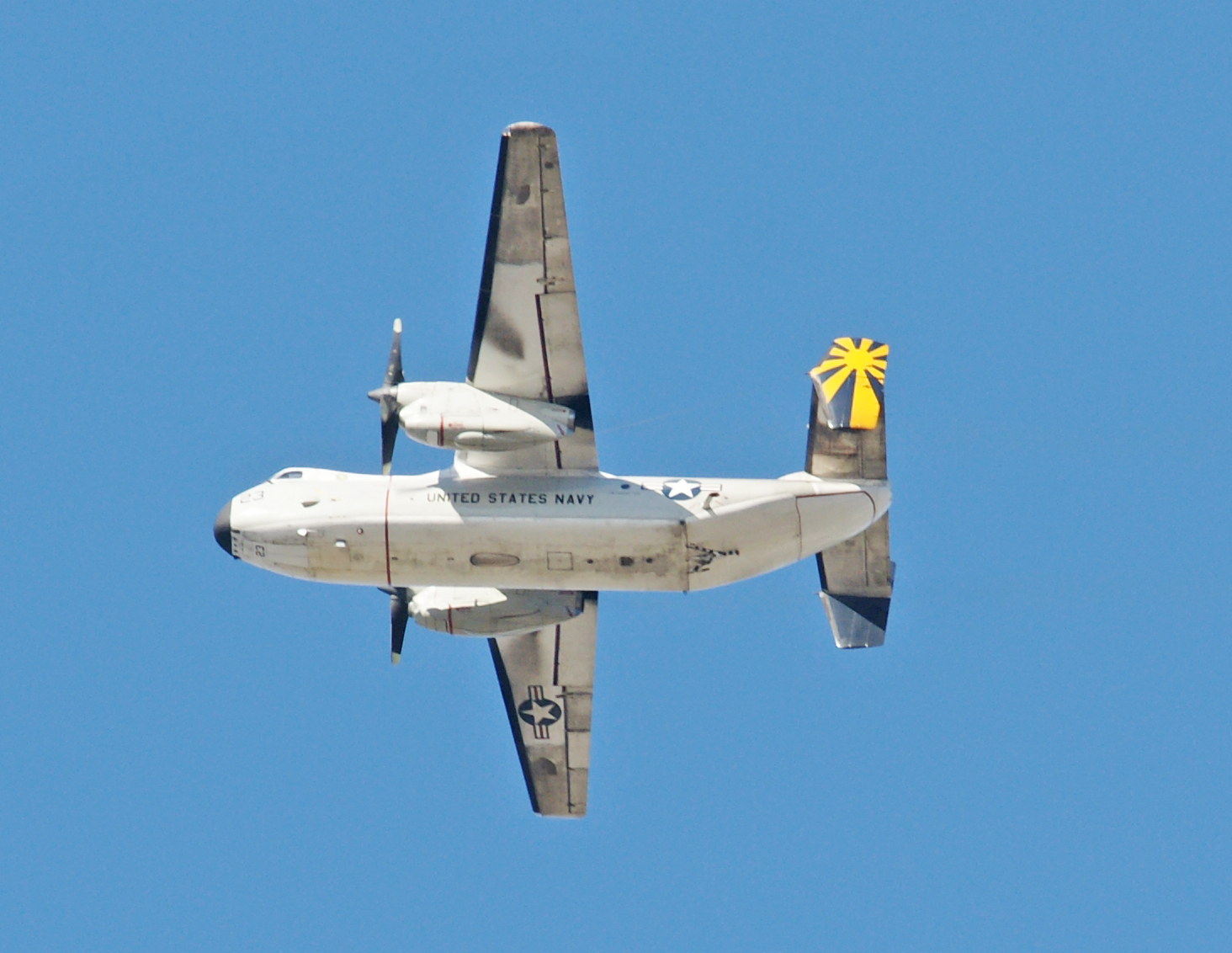
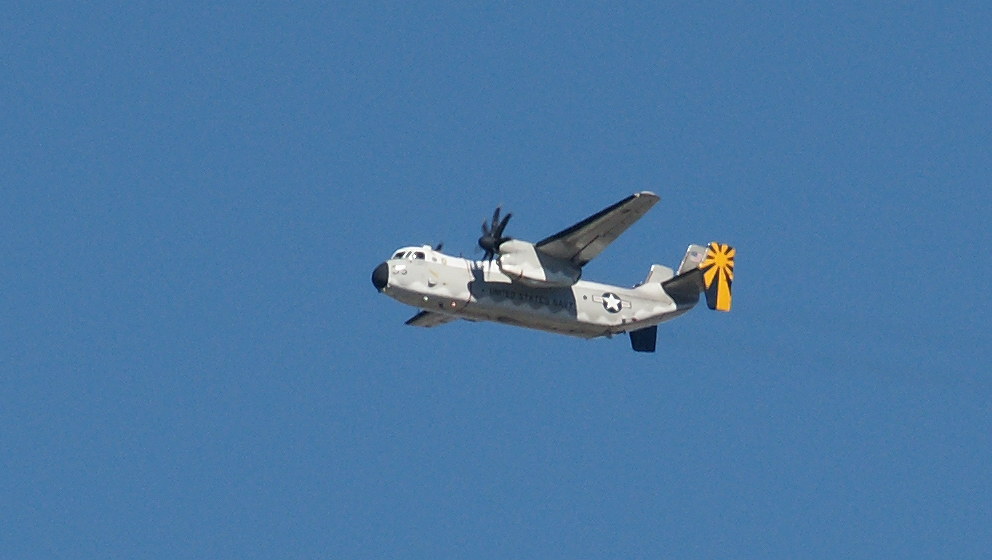
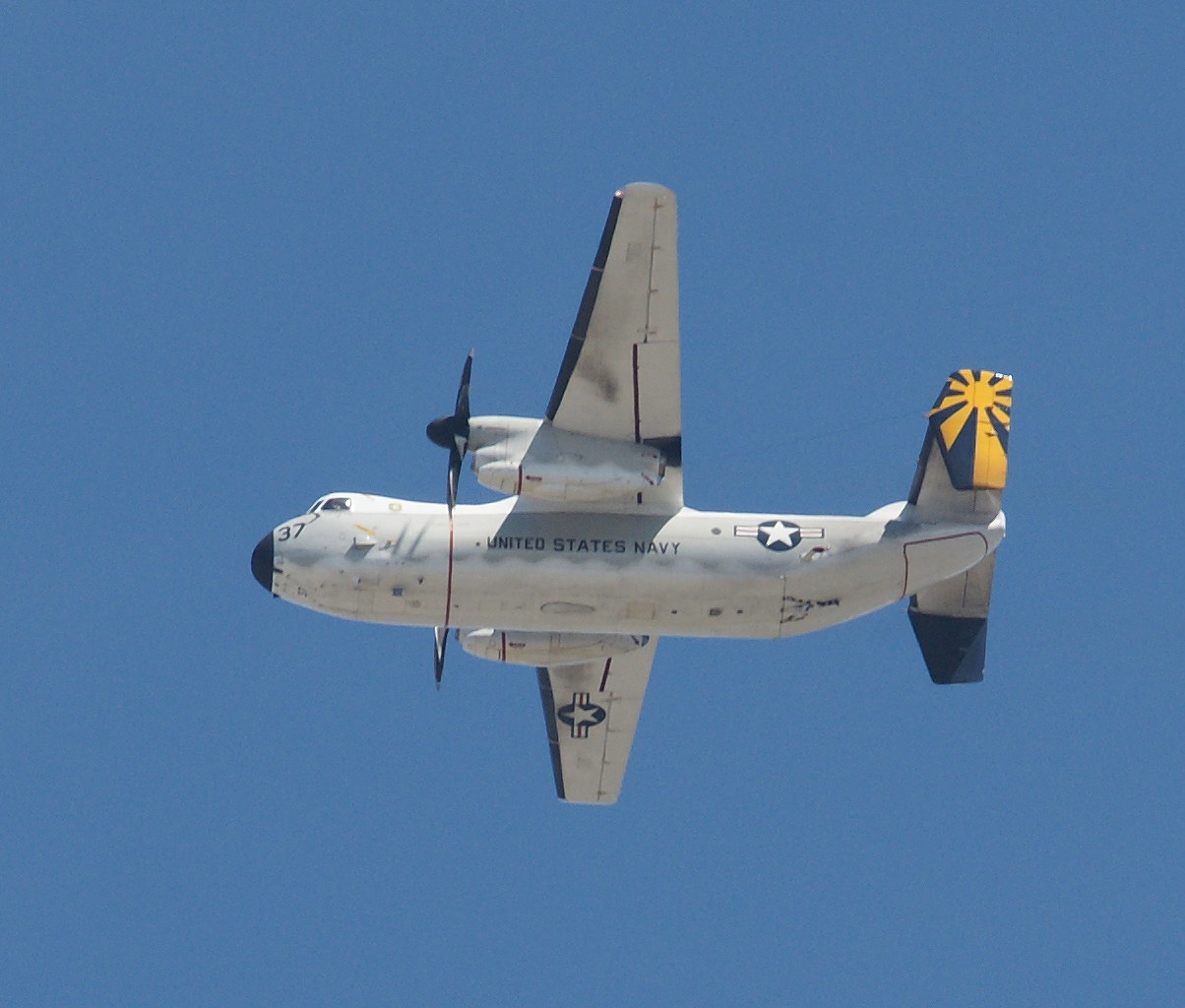
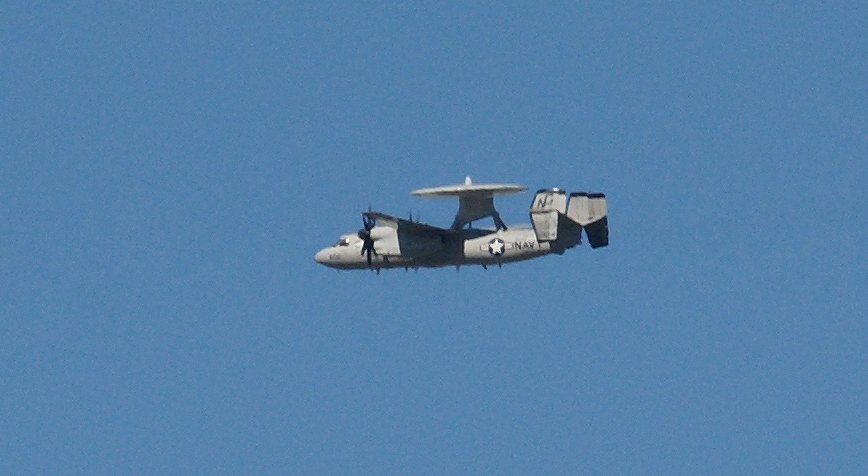
The Tracer was the first purpose-built airborne early warning aircraft used by the United States Navy. The aircraft was fitted with the Hazeltine AN/APS-82 in its radome and fuselage. The radar featured an Airborne Moving Target Indicator, which compares the video of one pulse time to the next in reflected radar energy to distinguish a flying aircraft from the clutter produced by wave action at the ocean’s surface. The Tracer was one of the first carrier-based early warning aircraft, and was used extensively in the Vietnam War.
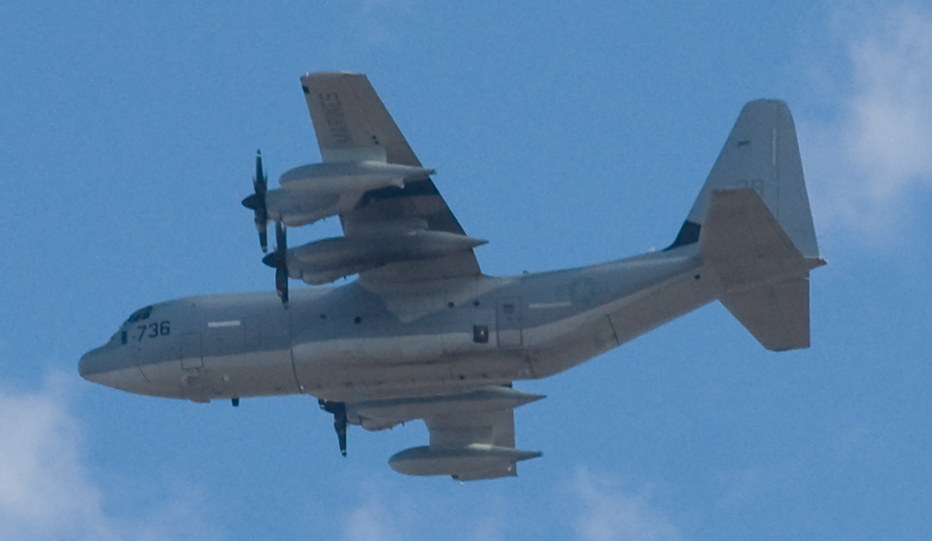
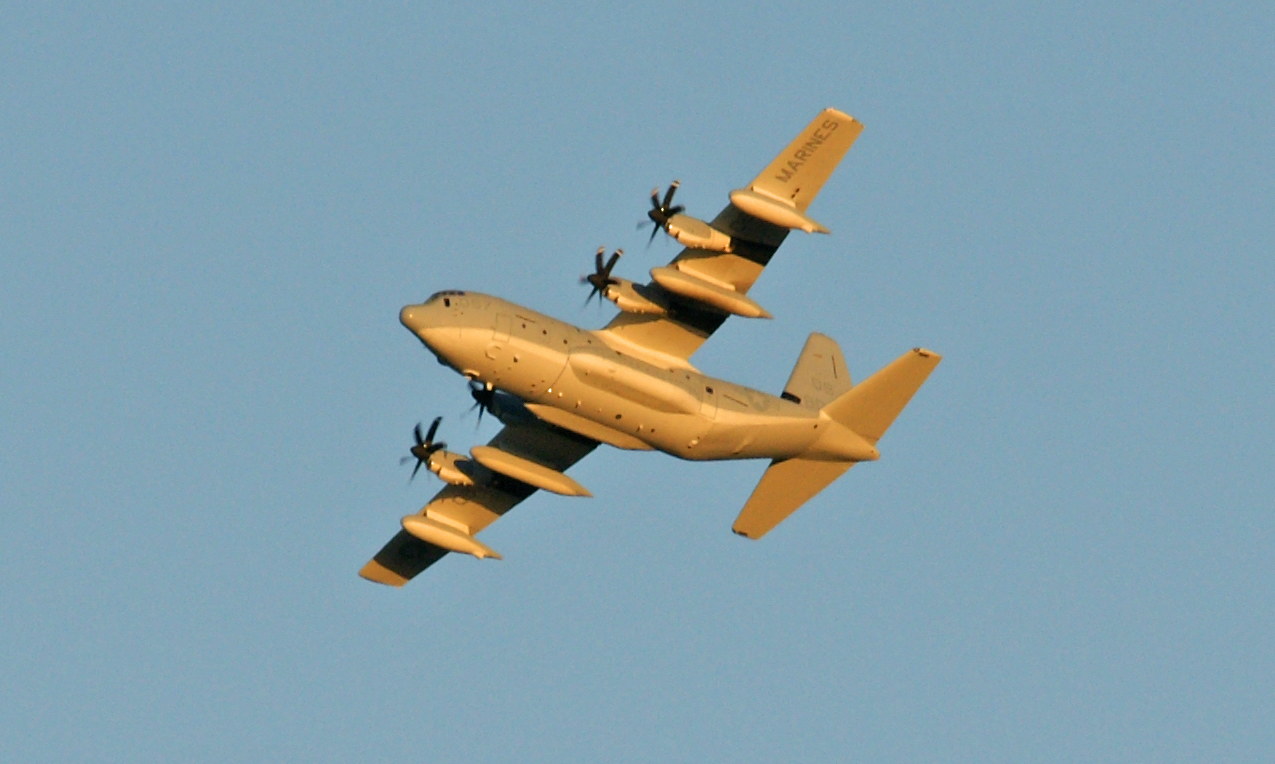
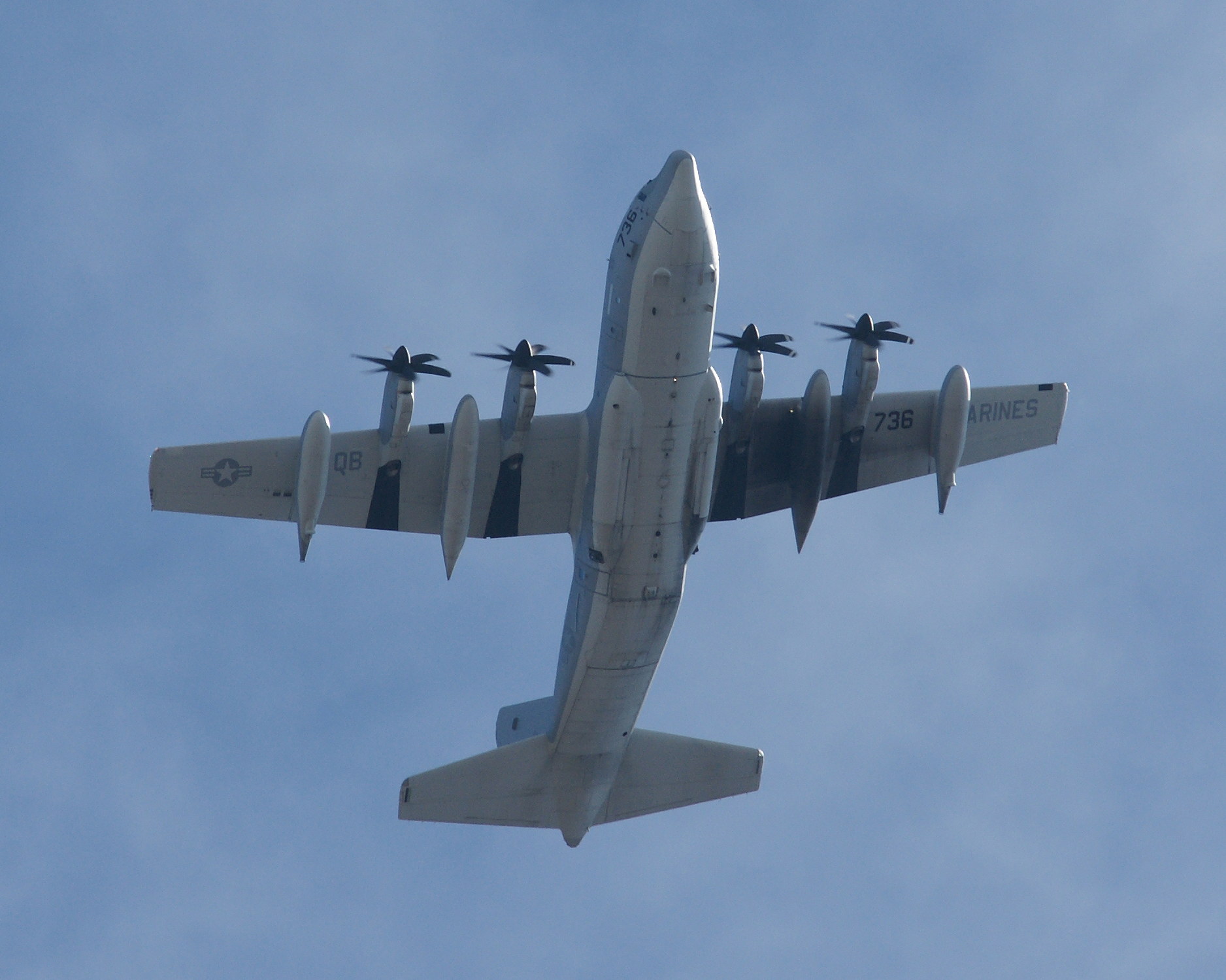
The Hercules is a four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, designed as a troop, medevac, and cargo transport aircraft. The versatile airframe has found uses in a variety of other roles, including as a gunship (AC-130), for airborne assault, search and rescue, scientific research support, weather reconnaissance, aerial refueling, maritime patrol, and aerial firefighting. It is now the main tactical airlifter for many military forces worldwide. Over forty variants and versions of the Hercules, including a civilian one marketed as the Lockheed L-100, operate in more than 60 nations.
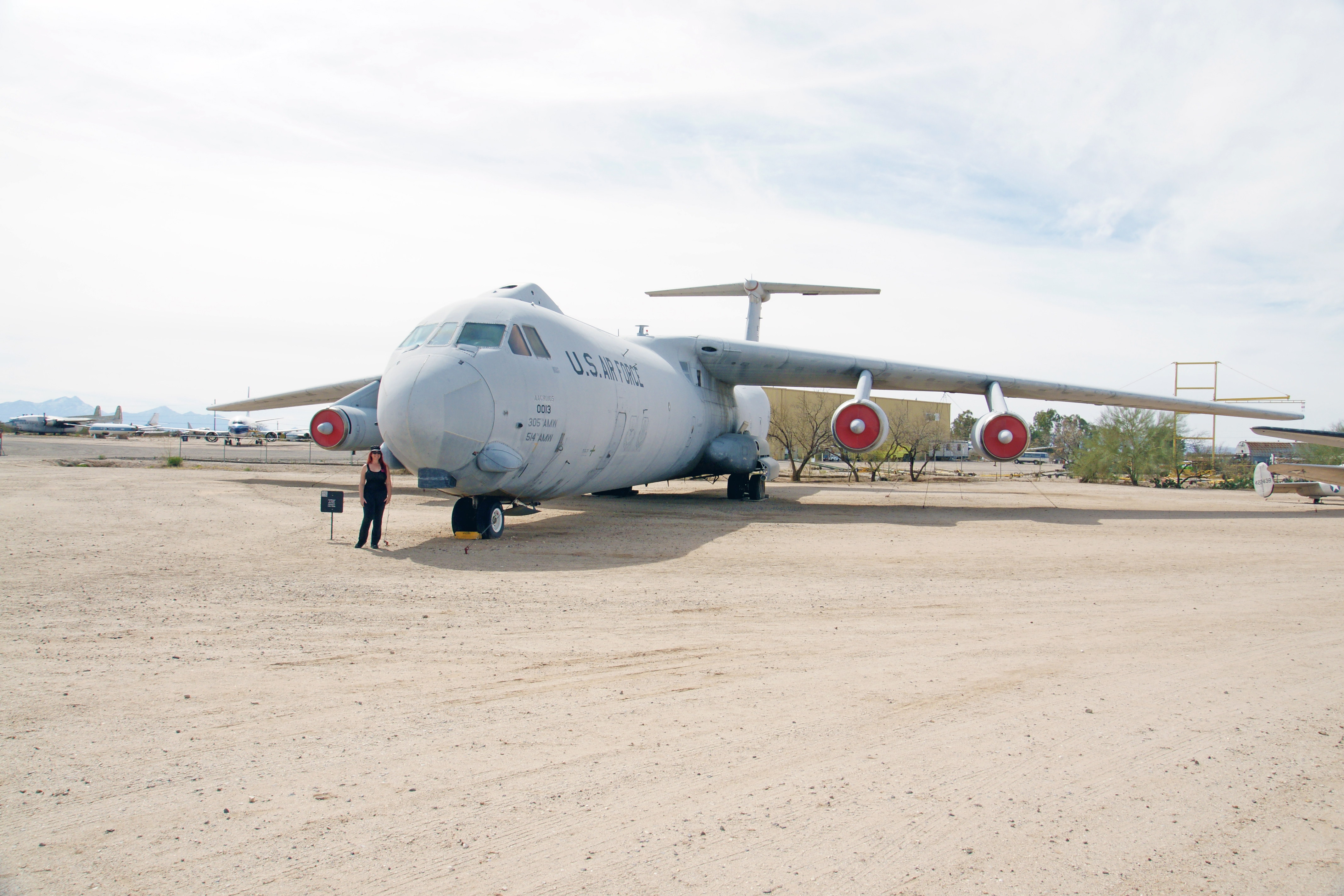
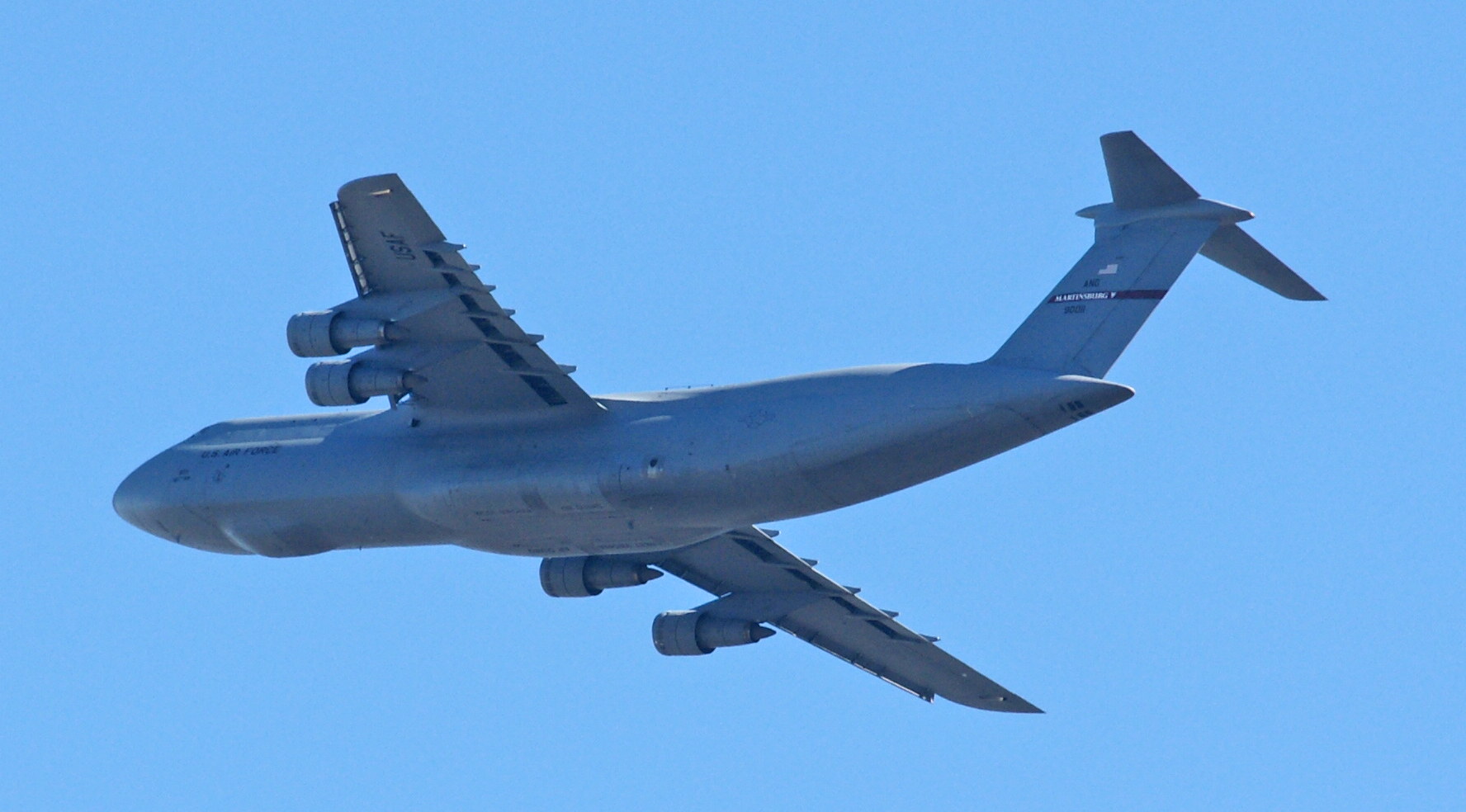
Introduced to replace slower propeller driven cargo planes such as the C-124 Globemaster II and C-133 Cargomaster, the Starlifter first flew in 1963. Eventually, 284 were produced for the Air Force, and one for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for use as an airborne observatory. The B version is over 23 feet longer than the A version, and has a boon receptacle for inflight refueling (seen on top of the aircraft just behind the cockpit).
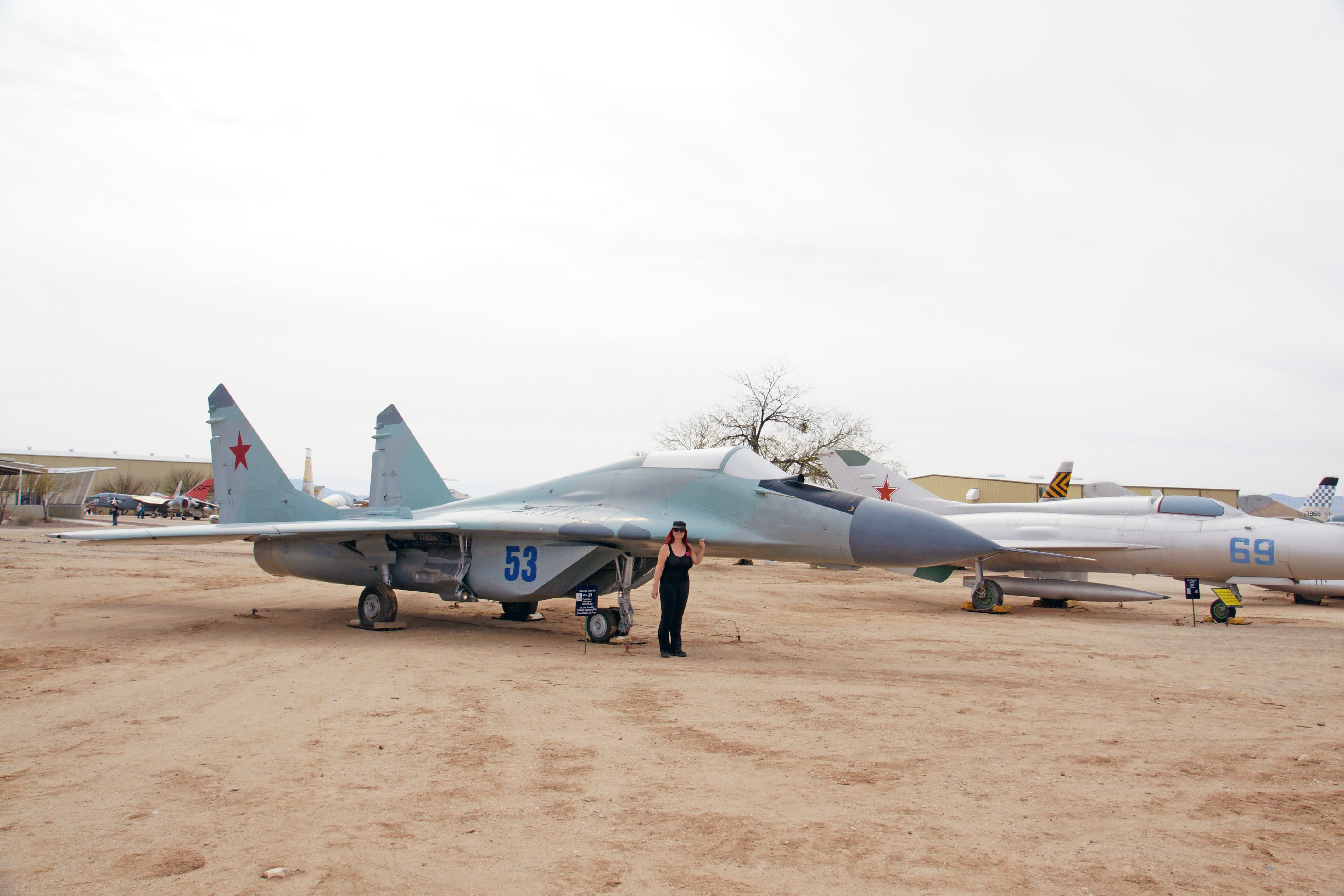
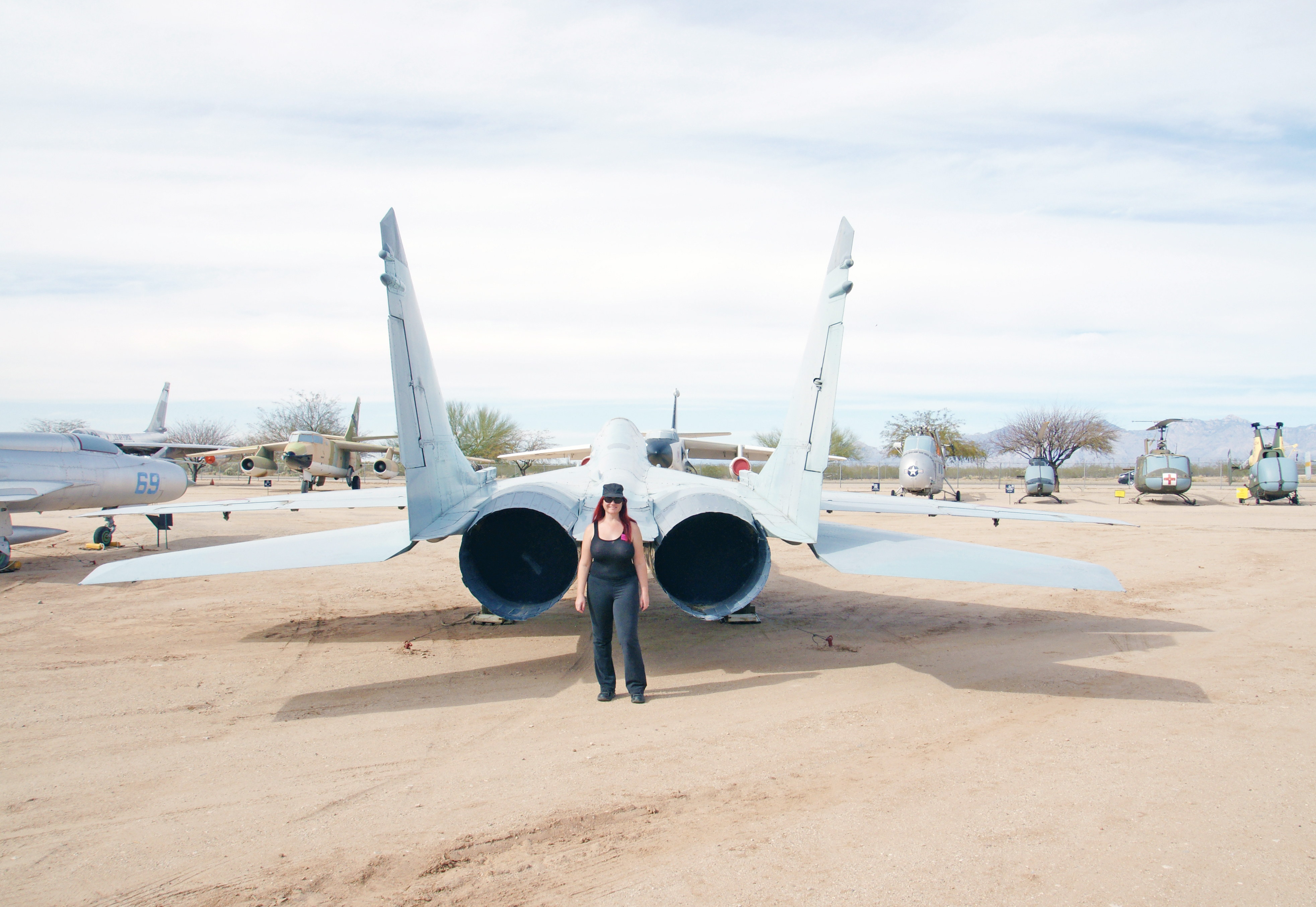
The MiG-29 Fulcrum is a twin-engine jet fighter aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. It was developed during the 1970s to counter new American fighters such as the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle, and the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon; it entered service with the Soviet Air Force in 1982.
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the militaries of a number of former Soviet republics have continued to operate the MiG-29, the largest of which is the Russian Air Force. The MiG-29 has also been a popular export aircraft; more than 30 nations either operate or have operated the aircraft to date, India being one of the largest export operators of the type.
The Fulcrum is powered by 2 Klimov RD-33 after-burning turbofans, 81.59 kN (18,342 lbf) each
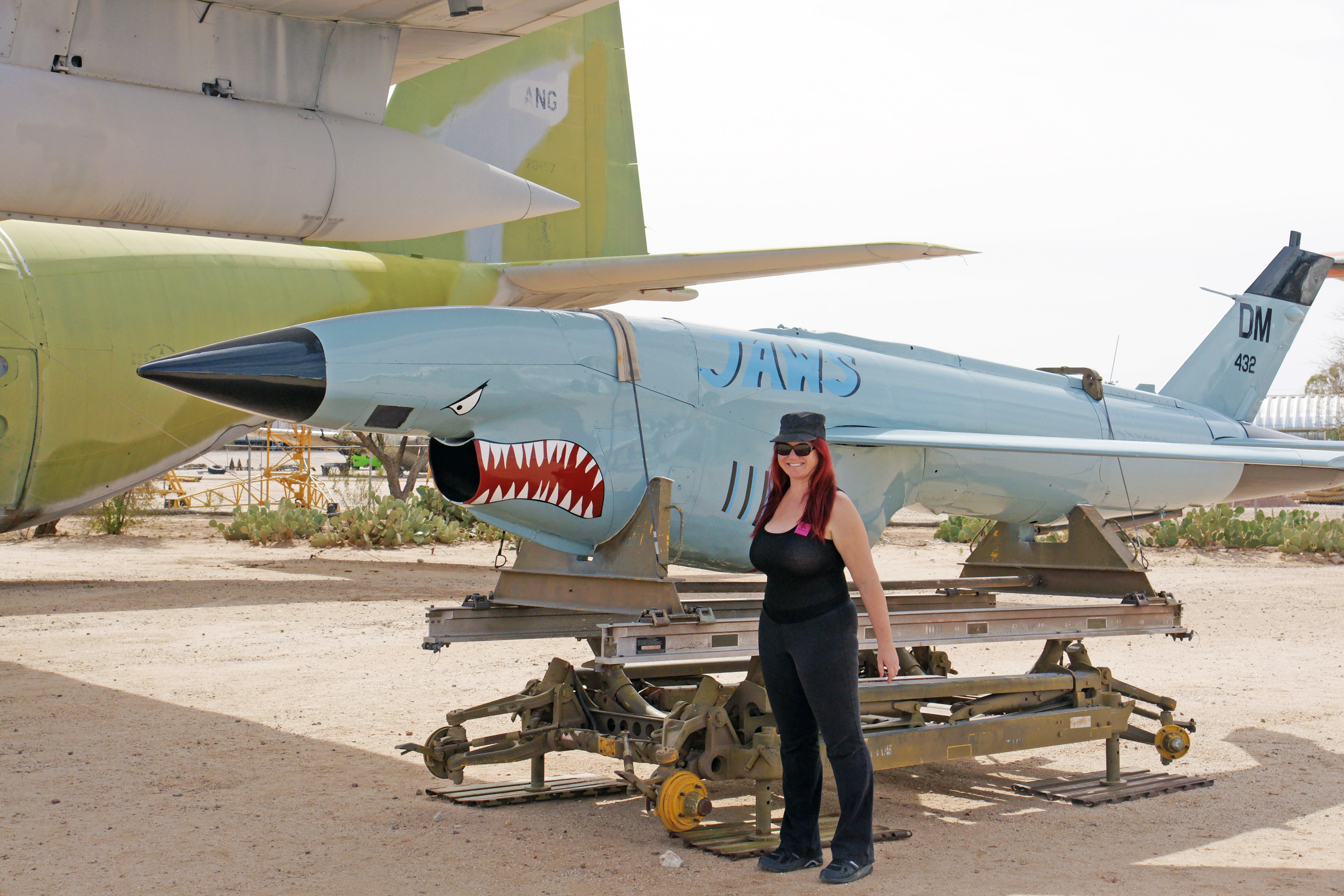
The Ryan Firebee was a series of target drones developed by the Ryan Aeronautical Company beginning in 1951. It was one of the first jet-propelled drones, and one of the most widely used target drones ever built. Over the decade between 1964 and 1975, the AQM-34 flew more than 34,000 intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance sorties over Southeast Asia during the Vietnam War—from Japan and China to Vietnam and Thailand.
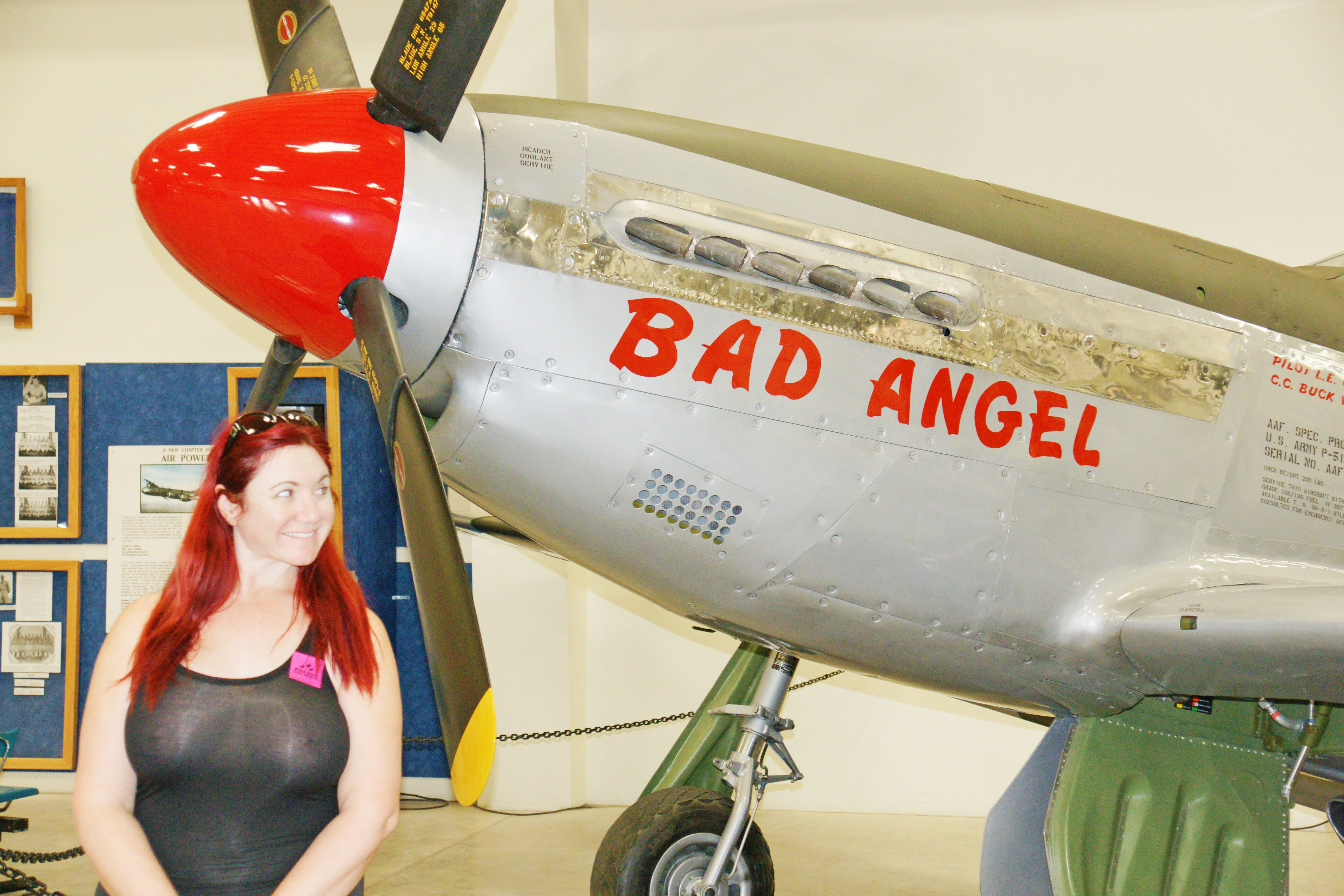
An iconic fighter plane in the Second World War, the Mustang “family” included almost 16,000 aircraft of 17 varieties, with over half of them being the P-51D, shown here. The Bad Angel was flown by Lt. Col. Louis E. Curdes, who shot down a C-47 that his girlfriend was aboard to prevent it from landing on a Japanese airstrip. The P-51D version was powered by the Packard V-1650-7, a license-built version of the Rolls-Royce Merlin 66 two-stage two-speed supercharged engine and was armed with six .50 caliber (12.7 mm) M2/AN Browning machine guns.
These are but a few of the aircraft at the Pima Air and Space Museum, which includes a B-17 Flying Fortress, B-29 Superfortress, C-119 Flying Boxcar, SR-71 Blackbird, and a 787 Dreamliner. We hope this small tease will encourage you to make a trip to Tucson and see for yourself.
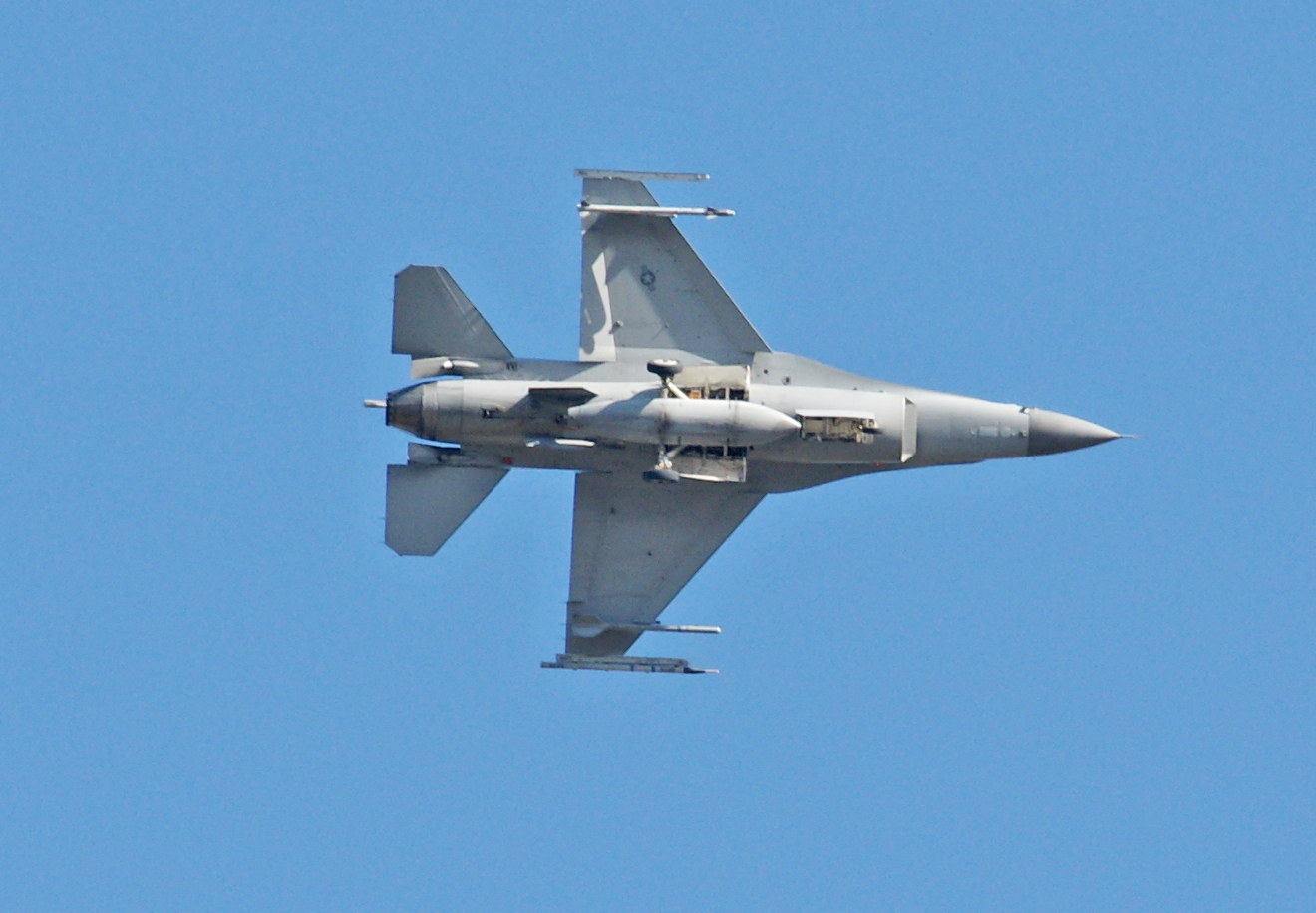
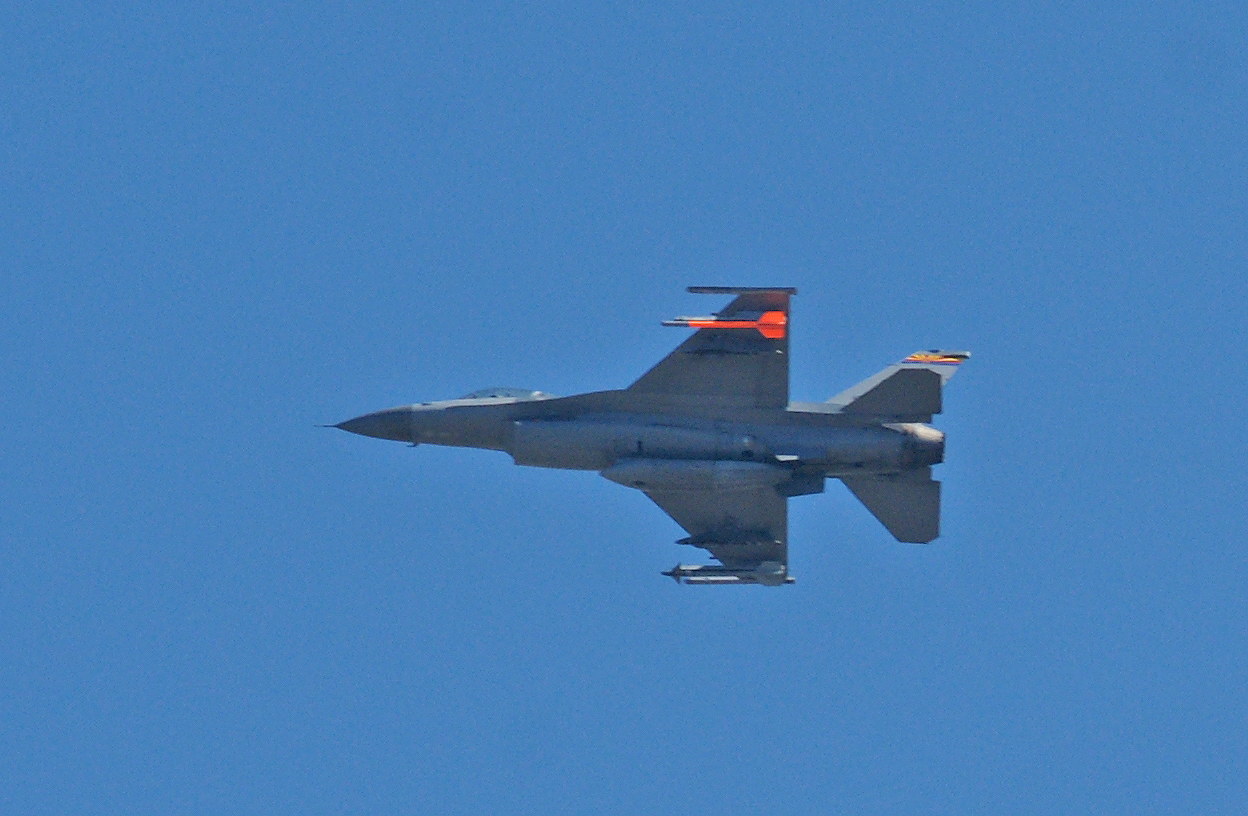
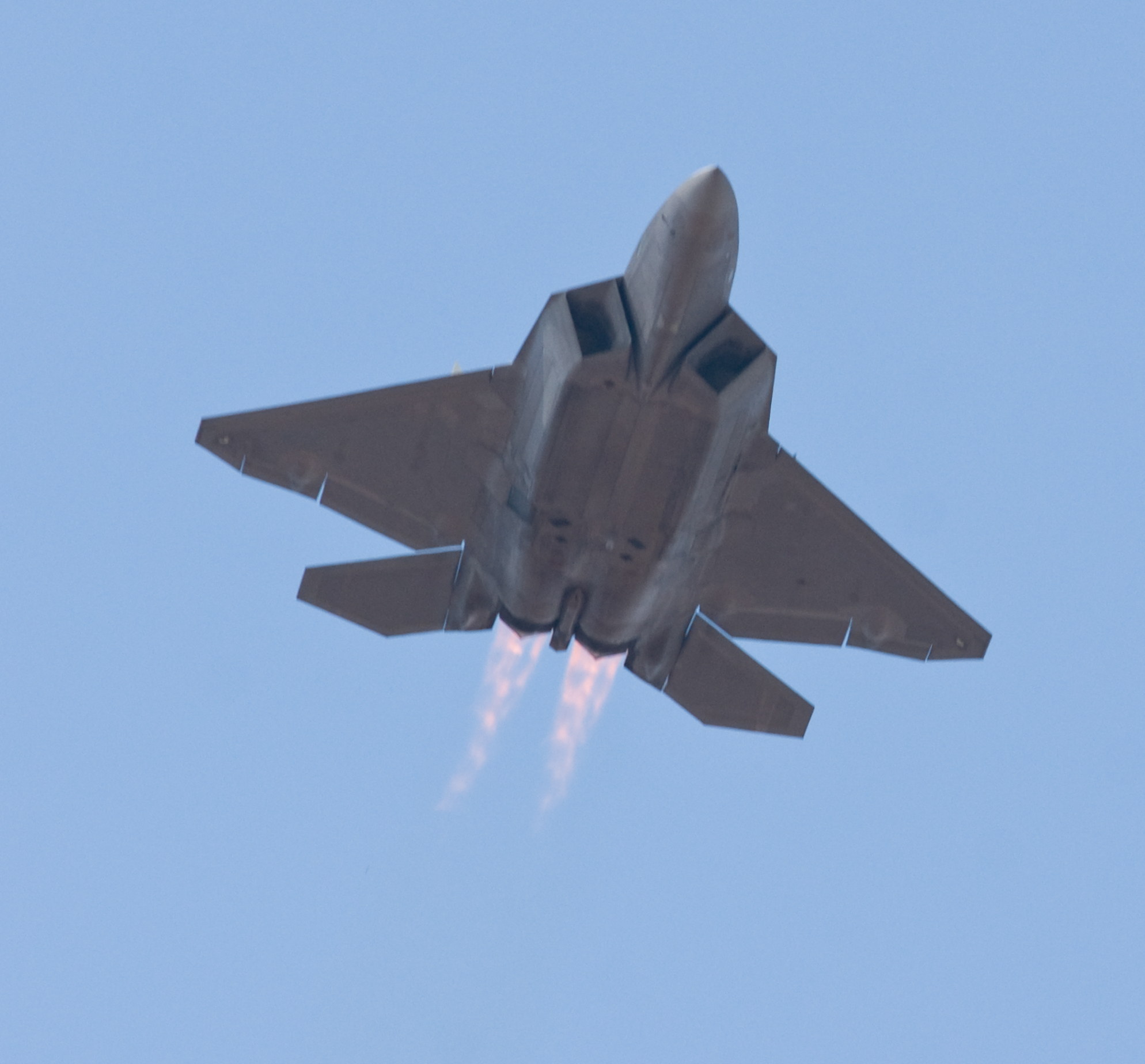
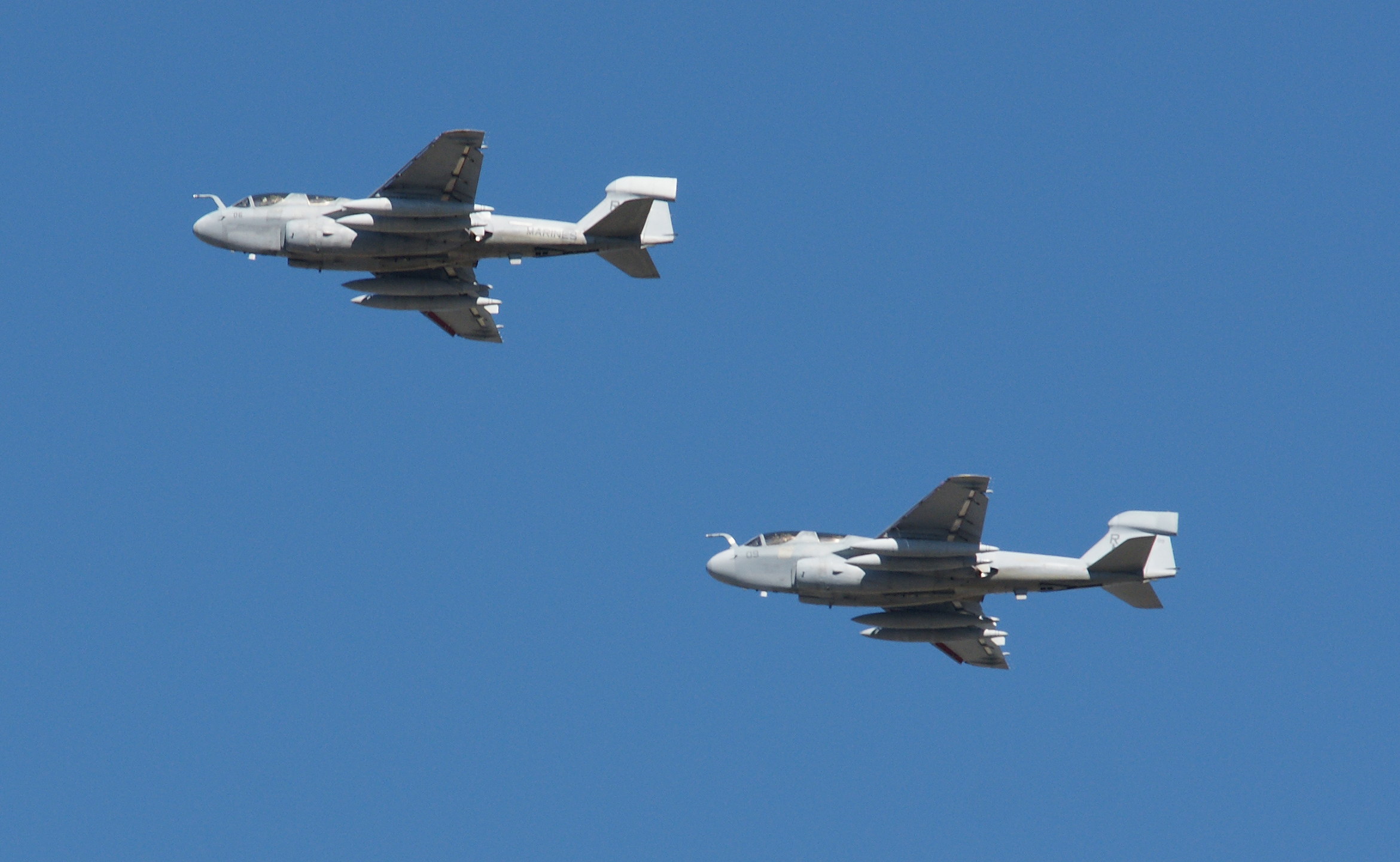
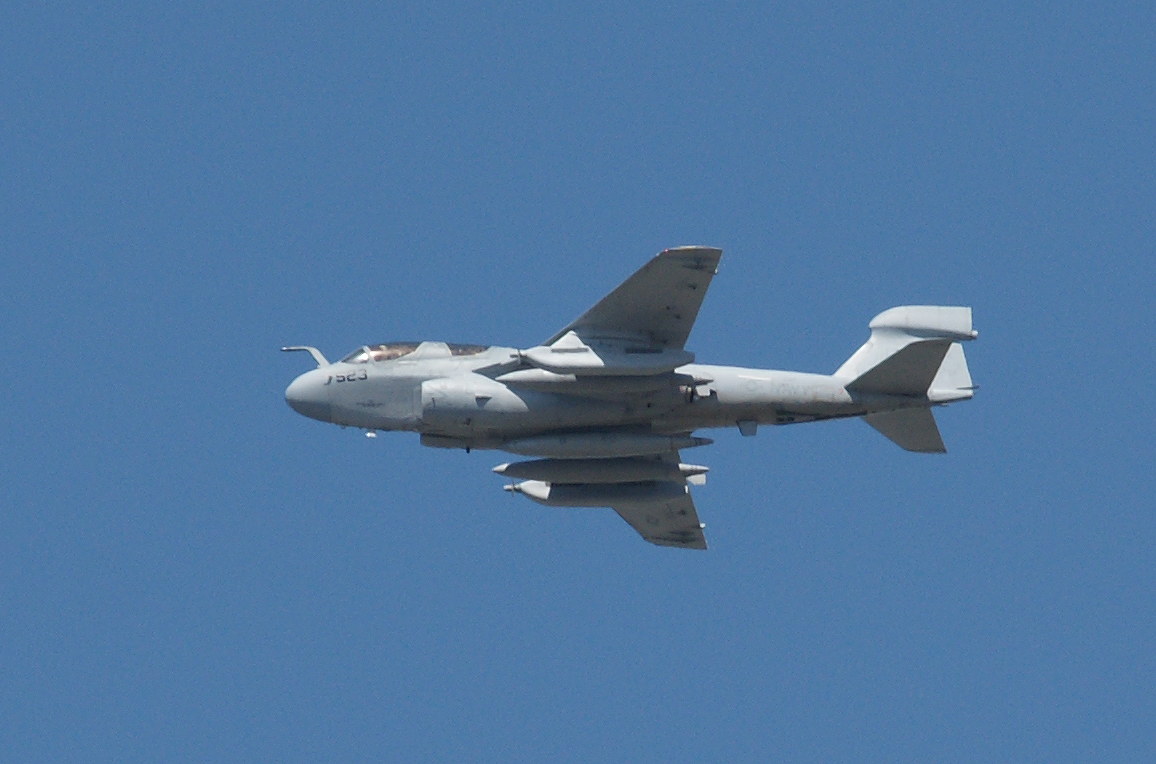
As long as you’ve come this far…some years ago, we lived in an apartment under the departing flight path of Miramar Naval Air Station, and took photographs of the aircraft every chance we could. Enjoy!